Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation
For basic views, structure, and targets, please refer to Environmental Management.
For performance data for environmental indicators , please refer to the CSR Book (ESG Data).
Information Disclosure Based on TCFD/TNFD
* TCFD:Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures, established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) at the request of the G20 (Summit on Financial Markets and the World Economy). It treats climate change as both a risk and opportunity and recommends disclosure of the impact that GHG-induced temperature rise has on corporate finances.
* TNFD:Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD), an international organization that develops a framework for assessing and disclosing risks and opportunities related to natural capital and biodiversity.

Decarbonization (GHG Emissions Reduction)
The Sumitomo Electric Group aims to achieve carbon neutrality for GHG emissions (Scope 1+2) from its manufacturing operations by 2050. As a milestone toward this goal, the Group set a 2030 target to reduce GHG emissions by 30% compared to FY2018 and is working to reduce emissions by 2.5% per year. For upstream and downstream GHG emissions in the supply chain (Scope 3), the Group aims to achieve a 15% reduction by 2030 compared to FY2018. These 2030 targets have been certified by the international initiative “Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi).”
<Transforming all plants into Net Zero Factories by 2050>
To achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, the Group established the Net Zero Factory Promotion Group within the Environment Department in 2023 to systematically promote the creation of a Net Zero Factory* model and its widespread adoption. The Group plans to transform all of its approximately 270 plants into net-zero factories by 2050, by promoting thorough energy conservation in production processes and expanding the introduction of renewable energy such as solar power.
* Net Zero Factory: A plant whose annual net GHG emissions are below zero and which is promoting energy conservation and energy creation at a level that serves as a standard for other plants, toward the goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050
Initiatives
Reduction of Scope 1+2 Emissions
The Group is striving to achieve its GHG emissions reduction targets by, in addition to promoting self-help efforts such as thorough energy saving, energy productivity improvement, and expansion of introduction of renewable energy including solar power, working to minimize risks while closely monitoring society’s GHG-related trends, such as changes in GHG emission factors of power companies and the supply-demand balance of green electricity.*
* Green electricity: Electricity generated using energy sources that do not emit greenhouse gases, such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power
Energy saving and energy productivity improvement are extremely important themes for companies, in terms of global warming prevention as well as cost competitiveness improvement. For this reason, the Group has set reduction targets not only for absolute amount of GHG emissions but also for reduction of energy consumption per basic unit, and is vigorously promoting energy saving as the foundation for GHG emissions reduction activities and production activities. Our energy saving activities focus on reducing fixed energy consumption that occurs regardless of production levels, and examining and introducing new energy-saving technologies.
Specifically, the Environment Department and business divisions hold quarterly dialogues on energy productivity improvement, where in addition to checking the progress in the reduction of energy consumption per basic unit, they discuss issues and share useful information on examples of new energy-saving technologies introduced, etc., thereby promoting resolution of issues. The information shared in the dialogues is disseminated across the Group via the Global Environment Promotion Conference, Decarbonization Portal Site, and other channels. In addition, to further promote productivity improvement, the Group is promoting investments in GHG emissions reduction projects by setting budget allocations for investments in CO2-reduction equipment and new technologies, while also implementing the “Energy Saving 200 Kaizen” activities to promote operational improvements.
One of the activities undertaken under “Energy Saving 200 Kaizen” is the reduction of standby power consumption by visualizing per-equipment energy consumption using IoT devices.
Furthermore, the Environment Department is working on the collection of information on, and evaluation of, new technologies that can ead to energy reductions to support the introduction of new technologies that meet each business division’s needs, with the aim of achieving significant reduction of energy consumption.
Regarding the introduction of renewable energy, the Group is systematically promoting energy creation through various means, including on-site (within company premises) and off-site (outside company premises) PPA,* based on the “Medium- to Long-Term Renewable Energy Procurement Guidelines” formulated by the Environment Department and the Procurement Division in FY2023.
* PPA: Power Purchase Agreement. A system in which electricity generated by power generation facilities installed and maintained by a power producer at its own expense is supplied to the user for a fee. In the case of on-site PPA, electricity is supplied from power generation facilities installed within
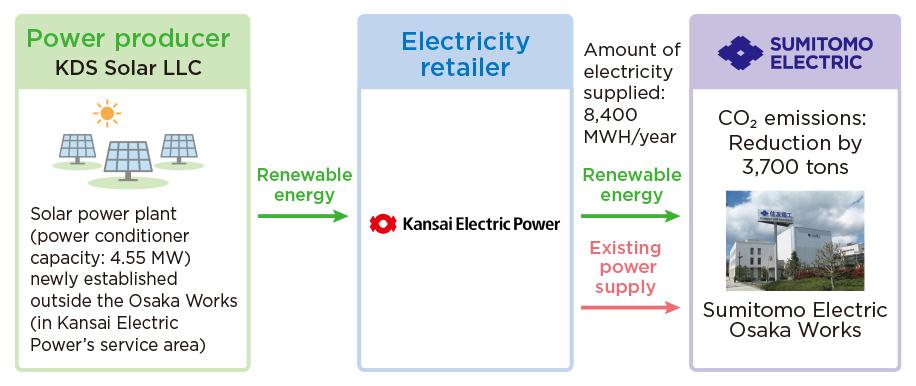
In February 2025, the Company signed its first off-site PPA contract. Starting in May 2025, Sumitomo Electric Osaka Works is supplied with renewable energy equivalent to approximately 13% of its annual electricity consumption from a solar power plant newly constructed by the Kansai Electric Power Company, Incorporated.

In Offices
We have reduced GHG emissions per floor area in offices through energy saving activities. Mainly to reduce the use of electricity, we have assigned a member and a vice member of the Workplace ECO Activity Promotion Committee in Osaka and Tokyo head offices, district offices and branch offices, and promoted various efforts as follows:
-
Moderating air conditioning usage by dressing cool in summer and warm in winter.
-
Turning off all office lights during lunch break
-
Turning off lights and air conditioners in meeting rooms and toilets when not in use
-
Turning off PCs when not in use.
Reduction of Scope 3 Emissions
The Group has more than 10,000 suppliers of raw materials and parts. To reduce Category 1 emissions, which account for approximately half of Scope 3 emissions, the Group has identified the top 100 emitters, focusing on manufacturers of materials such as copper, steel, aluminum, and synthetic resin, which account for a large proportion of CO2 emissions, as priority targets for its supplier engagement activities. Specific activities include explaining the Group’s policy to these suppliers and asking them to report their CO2 emissions and cooperate in emissions reduction.
Regarding CO2 emissions in Category 4 transportation, while responding flexibly to fluctuations in customer demand, the Group will continue to make steady efforts in expanding the use of rail containers and coastal shipping, improving truck loading rates, and reducing the number of trips. Furthermore, through the Green Logistics Subcommittee, which meets twice a year, the Group holds education sessions for Group companies to share information on the Group’s CO2 reduction performance in transportation and promote CO2 reduction activities across the Group.
LCA (Life Cycle Assessment)
The importance of product LCA is increasing due to a need for the improvement of competitiveness through reduction of product environmental impact and increasing requests from customers for disclosure of the carbon footprint of products (CFP). To respond to such a situation, the LCA Subcommittee was established directly under the Global Environment Promotion Conference in FY2023, and approximately 60 members are assigned to business units and departments to promote LCA. In FY2024, four Subcommittee meetings were held to share the latest information on LCA, including standardization in each industry, trends in the upstream and downstream supply chains, and examples of in-house LCA calculations. Through these activities, the Subcommittee contributes to promoting LCA and raising the level of LCA practice of the entire Group including improved calculation efficiency.
From FY2024, the Group is working to apply LCA in the development of products that achieve both reduced environmental impact and resource conservation, with examples including using LCA methods to evaluate the CFP reduction effects of using recycled copper in products that use copper.
Results
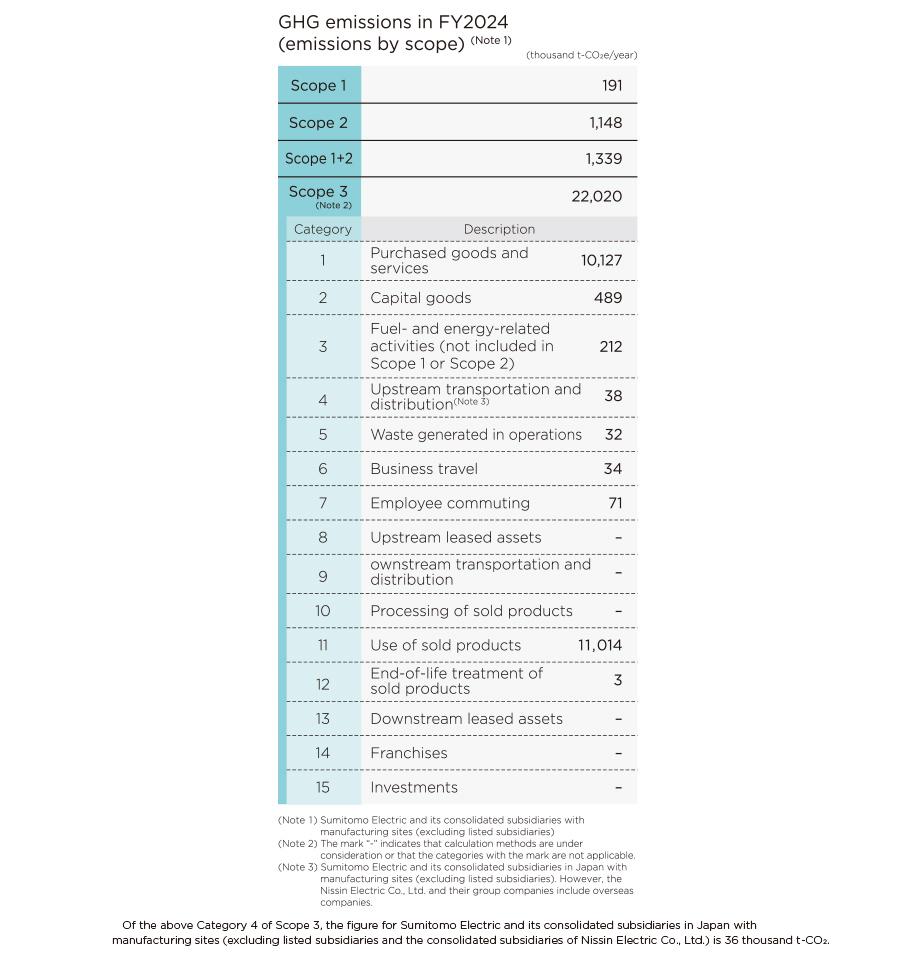
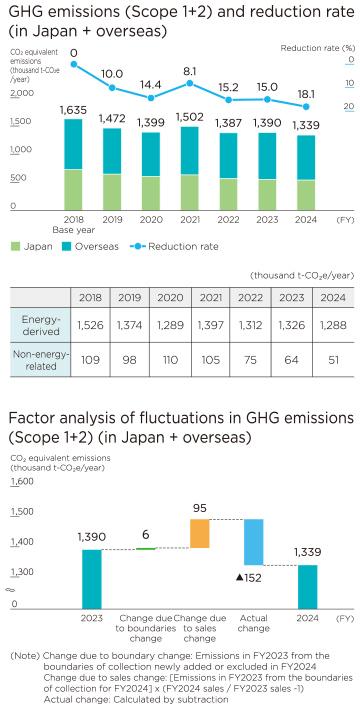
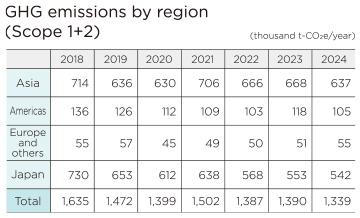
Reduction of Scope 1+2 Emissions
Against the FY2024 target of a 15% reduction compared to FY2018, the Group achieved an 18.1% reduction (20.4% decrease when listed subsidiaries included) in Scope 1+2 emissions. This is due, in addition to the reduction of GHG emission factors of the power companies, to our own efforts, such as promoting “Energy Saving 200 Kaizen” activities aimed at improving equipment efficiency and operational performance, introducing solar power generation facilities, and reducing non-energy-related GHG emissions such as sulfur hexafluoride (SF6).
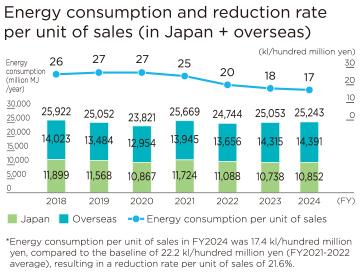
Energy Productivity Improvement
Although energy consumption in FY2024 was roughly the same as in the previous fiscal year due to active energy-saving activities at each division, the energy consumption reduction rate per unit of sales stood at 21.6% (*) compared to FY2018, exceeding the target of 6.6%, due to the significant increase in sales. By business unit, the Automotive Business Unit made a significant contribution.

Introduction of Renewable Energy
In FY2024, solar power generation facilities with a total capacity of 14.7 MW were installed in two locations in Japan and 14 overseas locations in Asia, Europe, etc., bringing the total installed capacity to 50.6 MW, exceeding the target of 30 MW.
Reduction of Scope 3 Emissions
In FY2024, Scope 3 emissions increased by 15.7% (1.1% increase when listed subsidiaries included), against the set emission reduction target of 7.5% compared to FY2018, meaning the target was not achieved. This is mainly due to increased product production.
<Strengthening of supplier engagement>
Of the top 100 emitters, 76 suppliers submitted an annual report on emissions data of products delivered to the Group. In addition to the top 10 suppliers with the highest emissions in the previous fiscal year, an agreement was obtained from the suppliers ranked 11th to 20th to develop and implement emissions reduction plans starting FY2024. Under the belief that supplier engagement is essential to reduce GHG emissions throughout the supply chain, the Group will continue working on supplier engagement on a top-priority basis.
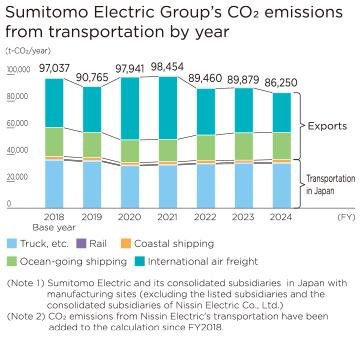
<Changes in CO₂ emissions from transportation>
In FY2024, total CO2 emissions from transportation in Japan and exports decreased by 4% from the previous fiscal year. CO2 emissions from transportation (by truck etc., rail, and coastal shipping) in Japan increased by 1%, while CO2 emissions from exports (ocean-going shipping and international air freight) decreased by 7.4%. The latter is due to the end of disruptions to ocean-going shipping (e.g. the lifting of transit restrictions), as well as the Group’s efforts to reduce the use of international air freight.
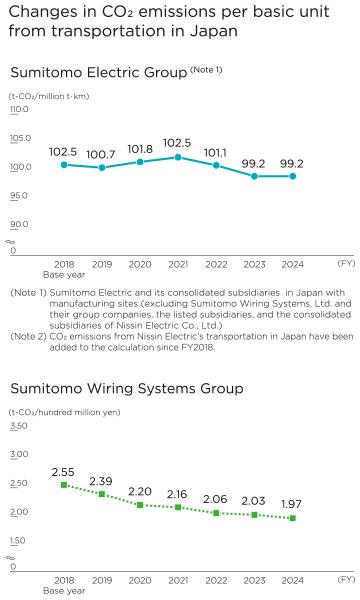

<Reduction of CO₂ emissions per basic unit from transportation in Japan>
Compared to the base year of FY2018, CO2 emissions per basic unit from transportation in Japan in FY2024 decreased by 3.3% in the Sumitomo Electric Group (see (Note 1) of the graph on the right) and by 22.5% in the Sumitomo Wiring Systems Group. The reduction rate of logistics CO2 emissions per basic unit in Japan, which totals the reduction rates for the two Groups above, was 12.7%, significantly exceeding the target of 6%.
The reduction rate for the Sumitomo Electric Group (see (Note 1) for the graph on the right) for FY2024 remained at the same level as the previous fiscal year mainly due to a significant decrease in the percentage of shipping use in some businesses caused by demand fluctuations, despite an increase in shipping use in some businesses other than the power cable and electric conductor business.
Going forward, the Sumitomo Electric Group and the Sumitomo Wiring Systems Group (see legend of the graph below) will continue steady efforts from a medium-to long-term perspective to reduce CO2 emissions from transportation.








