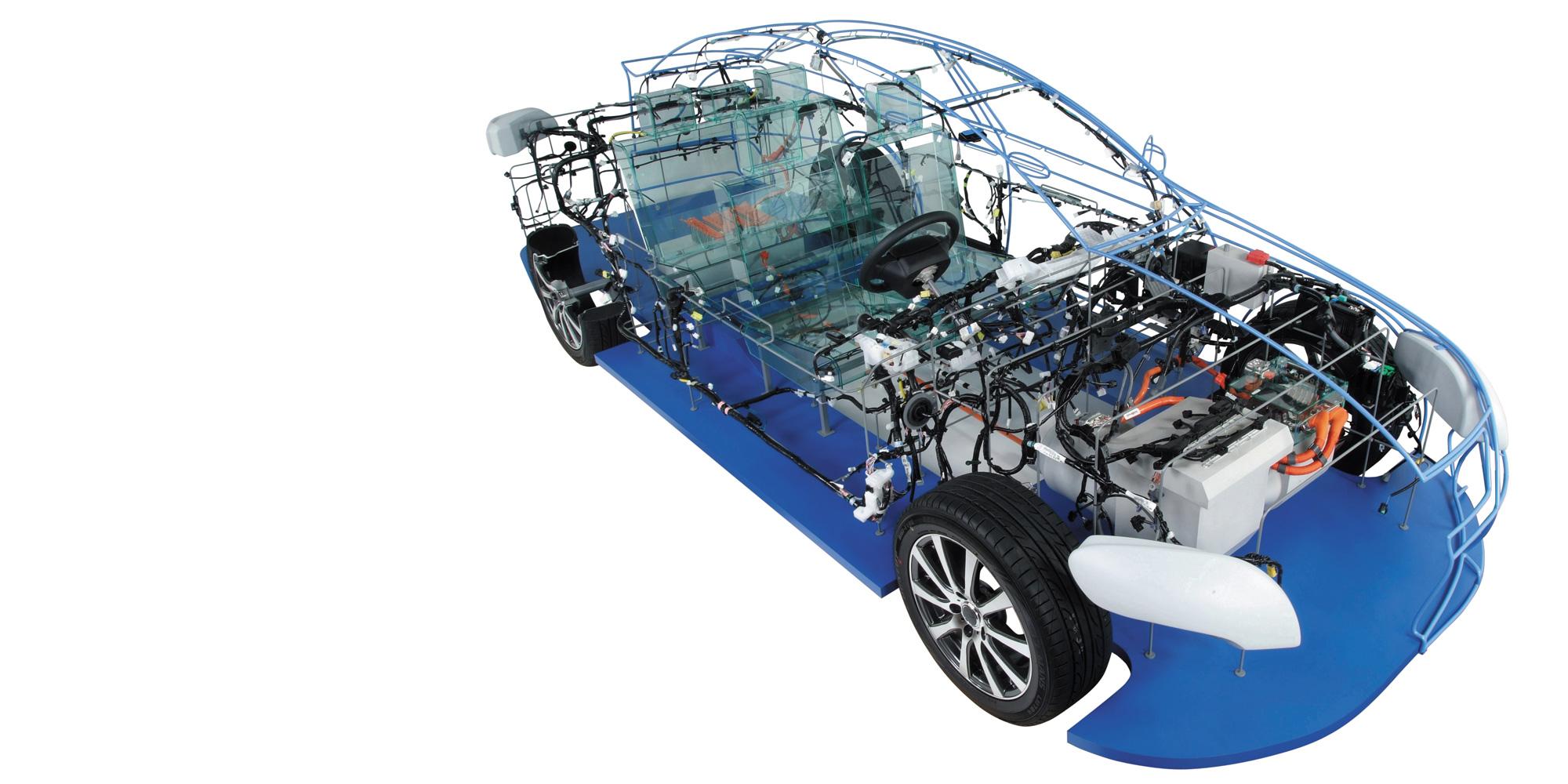

Challenges Toward “CASE” Innovation in the Auto Industry
Evaluating the reliability of wire harnesses and designing high-speed communication parts
Estimation of the fatigue life by CAE technology
The auto industry has been undergoing a once-in-a-century paradigm shift. CASE (Connected, Autonomous, Shared & Services, Electric) is the keyword of the trend. The Sumitomo Electric Group has been implementing various measures for CASE as a general automotive components supplier. This section focuses on CAE of wire harnesses, which are the main products, and connectors, which are used to connect wire harnesses.
Many wire harnesses are used for in-vehicle wiring of automotive components. They form a system to transmit energy and information. Their functionality is equivalent to that of the nervous system and blood vessels in the human body. The reliability evaluation was one of the major issues. The service life until fatigue disconnection occurs is one of the reliability factors. Notably, reliability evaluation of door wire harnesses, which are frequently moved by open-close motions, was a major issue. The Sumitomo Electric Group started simulation to estimate the fatigue life of cables by bending motions in the 1990s. Shigeki Shimada, Manager of the Osaka Analysis Dept., has been engaged in development of CAE techniques since the 1990s.

“The reliability requirements of automakers became more stringent than before around 2000. At that time, the competition among wire harness manufacturers to develop CAE technologies intensified. We were outstripped by competitors in the technology to estimate the fatigue life of a cable. Customers criticized us for being 10 years behind competitors. Under these circumstances, the ATRC was launched by integrating the analysis team with the CAE team and embarked on the development of more accurate CAE in collaboration with Sumitomo Wiring System, Ltd., which was in charge of experiment and verification. A turning point came when new CAE techniques were established by using X-ray CT to visualize the wire shape in cables and identify the locations that were likely to be damaged in cables and the factors that dominated the fatigue life,” said Shimada
At present, the ATRC is highly evaluated by automakers, which are our customers, for its CAE technologies that are among the highest in the industry.
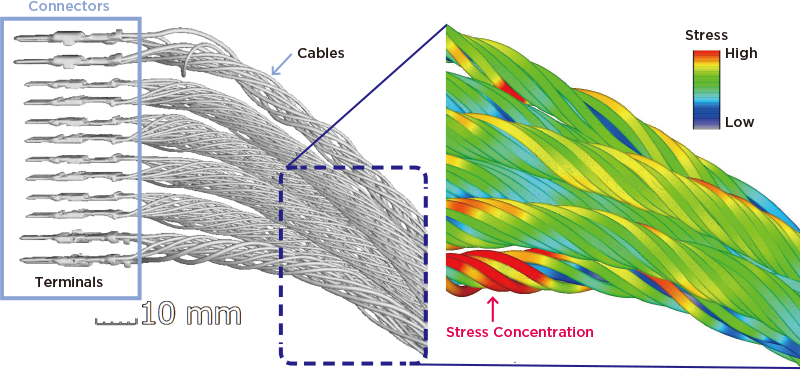
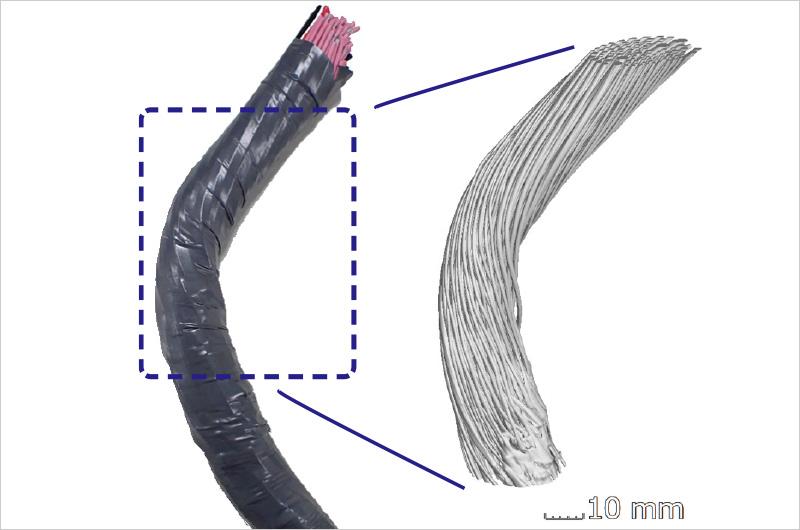
Wire harnesses changing due to the big trend in EVs
Reliability evaluation of wire harnesses is important because it is directly linked to the safety and security of vehicles. Namely, wire harnesses are expected to ensure reliability without causing disconnection until the end of the service life of vehicles. Yuki Tanaka, Manager of Wiring Harness Reliability Section, Experiment & Evaluation Dept., Sumitomo Wiring System, Ltd., commented as follows:

“Recently, new model cars have been developed in shorter periods than before. Meanwhile, the flex durability requirements of wire harnesses have become more rigorous. It is difficult for wire harness manufacturers, including Sumitomo Electric, to secure time for design rework. This necessitates the use of CAE in the design phase. CAE plays a key role in solving problems in advance based on simulation. In competitive bids to receive orders, suppliers are required to verify reliability by using simulation technologies. We will further advance simulation technologies and train personnel who can use such technologies to organize a strong CAE team,” said Tanaka.
Soichiro Okumura, who is in charge of development of CAE techniques in the Osaka Analysis Dept., worked with Shimada on CAE-based technologies to estimate the fatigue life of wire harnesses. He said that the developments in CASE have brought about a new phase in CAE for wire harnesses.

“EVs, which represent ‘Electric’ in CASE, require large currents. Inevitably, they require thick cables. While conventional in-vehicle cables for energy transmission consisted of dozens of wires, cables for EVs consist of up to thousands of wires and have complicated structures. We estimate the locations that are likely to be damaged and disconnected. These efforts also aim to establish know-how for extending the service life of cables. The wires are stranded and bent in various ways, and this affects the performance and efficiency of the manufacturing process. We hope to achieve highly reliable cables required for EVs by taking full advantage of CAE,” said Okumura.

Development of high-speed communication connectors by using CAE
“Connected” in CASE refers to “connected cars.” Various kinds of data, including the vehicle condition and road condition around the vehicle, are obtained from sensors to create value in various ways. In-vehicle wire harnesses transmit information to achieve connectivity. The key point here is that the frequency of transmitted signals has been increasing in line with the increase in communication speed and capacity. Smooth transmission of signals is indispensable to achieve connectivity. Masanao Yamashita, who is affiliated with the Connected Technology Development Promotion Dept. of the CAS-EV Development Promotion Divison, has been working to meet this challenge
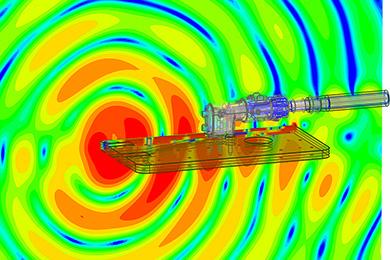
“Connectors take on a role for connecting wire harnesses that are routed throughout a vehicle. In high-frequency communication, electric signals which have extremely short wavelengths are transmitted in very short time. Signals are significantly affected by electrical disturbances of the signal path mainly caused by connectors. They may be attenuated by reflection, resulting in communication mismatches. Thus, the connector shape must be designed to ensure smooth signal throughput. CAE is used in this process. We use CAD to design the shape, which is loaded into the analysis software in the computer. We then configure the communication conditions and perform finite element analysis (FEA) by fragmenting the analysis target into many small elements called "mesh," which is one of the CAE techniques, to derive the optimal shape of a connector. This is one of the means to achieve connected cars,” said Yamashita.
Calculation, on which Yamashita works, is one of the challenges. In CAE, the mesh size must be finer to represent the higher frequency, whose wavelength is shorter. The calculation required in analysis and the amount of data handled have been increasing continuously. Efforts have been made to develop CAE technologies and build a system in anticipation of next-generation CAE, including the upgrade of the equipment.
The Sumitomo Electric Group’s efforts related to analysis technologies, which have been discussed above, are just examples. The ATRC handles all products in all the business fields. Superb analysis technologies help ensure a competitive advantage. Evolution of analysis technologies is driven by a sense of mission of each researcher to guarantee high product reliability and contribute to better manufacturing operations. Sumitomo Electric will continue to take on challenges to fulfill the mission.

Registration of public notification
If you register your e-mail address, we will notify you when the latest issue is published. If you wish, please register from the registration form.
To delete your registration, please visit here.
