Featured Stories
The Smart Choice for Long-Term Energy Savings
As the U.S. accelerates its shift towards renewable energy, the need for reliable, long-term energy storage solutions has never been greater. The energy industry is undergoing a significant transformation as renewable energy sources like wind and solar become more prominent. However, these intermittent energy sources present challenges for a grid designed around steady, controllable power generation. This article explores the current energy landscape in the U.S., the necessary steps to ensure a sustainable energy future, and how Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries (VRFBs) offer a compelling solution to these challenges.

◇ The U.S. Energy Reality
The United States is in the midst of a monumental energy revolution, driven by the simultaneous demands for clean, carbon-free energy and the urgent need to stabilize the nation’s aging power grid. As industries and households increasingly shift towards greener energy, several important challenges come to the forefront.
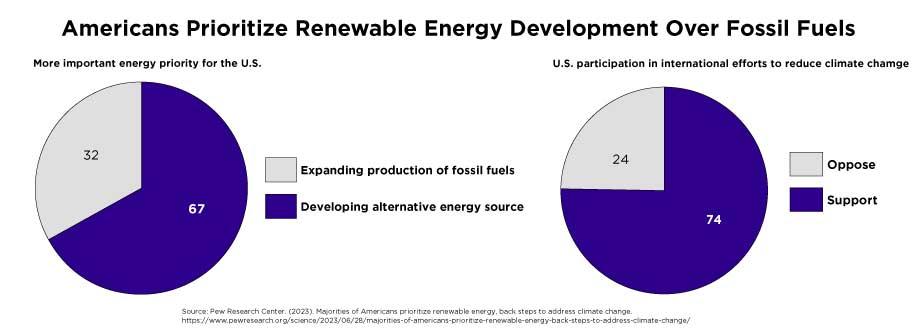
Growing Demand for Clean Energy: Public support for renewable energy is strong and growing. A 2023 Pew Research Center study found that 67% of American adults now prioritize developing alternative energy sources like wind, solar, and hydrogen over fossil fuel production. This strong public support highlights the need for cleaner energy to fight climate change.
Grid Instability: With more renewable energy sources integrated into the grid, balancing demand and supply becomes highly challenging. Intermittent sources like solar and wind require effective long-term energy storage solutions to avoid grid overloads or shortages.
Support for Climate Action: According to a 2023 Pew Research Center survey, 74% of Americans support U.S. participation in global climate change efforts. This strong public backing highlights the urgency for innovation in energy storage and grid infrastructure, especially as we reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Energy Safety and Security: While lithium-ion batteries have played a valuable role in short-duration energy storage, the increasing reliance on renewable energy sources highlights the need for further innovation, particularly in LDES. Ensuring both the safety and longevity of storage technologies will be key in supporting this transition.
◇ What Needs to Be Done to Secure the Future
Several key actions are essential to meet the growing energy demand while addressing climate challenges.
Accelerating LDES Deployment: Advancing long-duration energy storage (LDES) technologies is essential to guarantee that renewable energy sources can reliably meet future demand. Public interest in these developments is growing, with 67% of Americans prioritizing alternative energy development (Pew Research Center). The push for innovation in LDES is especially significant as it directly addresses the need for stable, scalable energy storage solutions, a critical component in America's journey toward energy independence and resilience.
Modernize the Power Grid: The U.S. power grid is outdated and often struggles to handle the increasing load from renewable energy sources. Infrastructure modernization is critical to support distributed power generation and efficiently store and use clean energy. This will improve grid stability and accommodate the growing use of variable renewable energy (VRE) sources like wind and solar.
◇ How Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries Might Provide a Solution
Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries (VRFBs) offer innovative solutions to energy storage challenges and several key advantages over conventional battery technologies:
Long-Duration Energy Storage: VRFBs can store large amounts of energy for extended periods with minimal degradation, making them ideal for long-duration energy storage (LDES). As the U.S. integrates more variable renewable energy sources like solar and wind, VRFBs are well-suited for storage durations of 6+ hours, where lithium-ion batteries lose feasibility. VRFBs excel by decoupling energy capacity from power output, simply by scaling the electrolyte volume.
Enhanced Safety and Sustainability: One standout feature of VRFBs is their superior safety profile. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, VRFBs operate at lower temperatures and use non-flammable electrolytes, reducing the risk of fires. Their recyclable electrolytes further align with the push for environmentally friendly energy solutions. Given Americans’ growing support for policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions, safer and greener technologies like VRFBs are gaining attention.
Lower Levelized Cost of Storage (LCOS): Over their long operational life, VRFBs offer a significantly lower levelized cost of storage compared to lithium-ion batteries, particularly for long-duration storage. This makes them not only safer and greener but also more cost-effective for large-scale energy storage applications.
As the demand for reliable, long-duration energy storage grows with the rise of renewable energy, VRFBs are well-positioned to meet these challenges. Their stable, scalable, and safe solutions pave the way for a more resilient and sustainable energy grid.
◇ Conclusion
The transition to a sustainable energy future in the U.S. depends on overcoming the intermittency of renewable energy sources and modernizing the nation's power grid. Long-duration energy storage technologies are essential to achieving this goal.
Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries (VRFBs) offer a unique solution to these challenges, combining scalability, safety, and cost-efficiency to meet the growing demand for reliable energy storage. By embracing VRFBs and continuing to modernize energy infrastructure, the U.S. can unlock the full potential of renewable energy, ensuring a cleaner and more secure power supply for decades to come.
References:
Majorities of Americans Prioritize Renewable Energy, Back Steps to Address Climate Change – Pew Research Center
Follow us on LinkedIn!
If you enjoyed this Feature Story, be sure to follow Sumitomo Electric U.S.A on LinkedIn. We share updates there whenever new stories are published. (Note: Sumitomo Electric Group also has a global LinkedIn account for corporate updates.)






