Terminology related to Optical Fibers

Terminology
The terminologies for optical fibers are as follows.
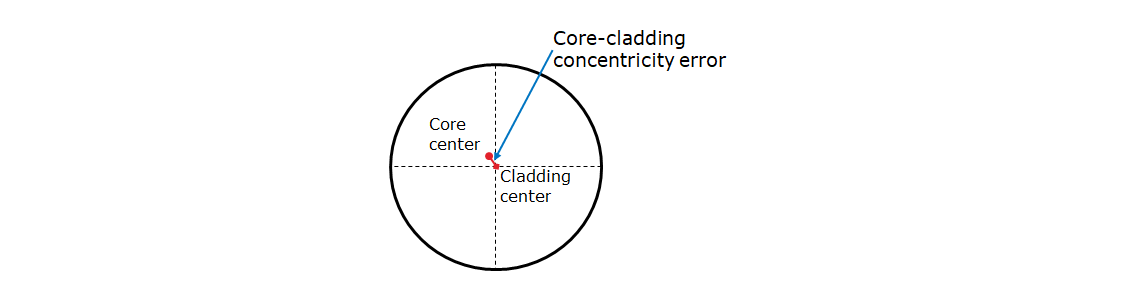
Core-Cladding Concentricity Error
Core-cladding concentricity error is defined as the distance of the center position between the core and cladding. Smaller core-cladding concentricity error is preferable for minimizing splice/connector loss.
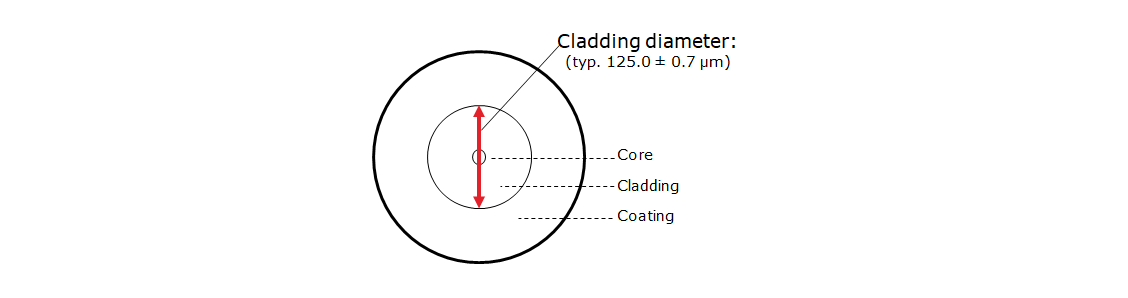
Cladding Diameter
Cladding diameter is defined as the outer diameter of the optical fiber's glass section, which is the vertical red line in the diagram.
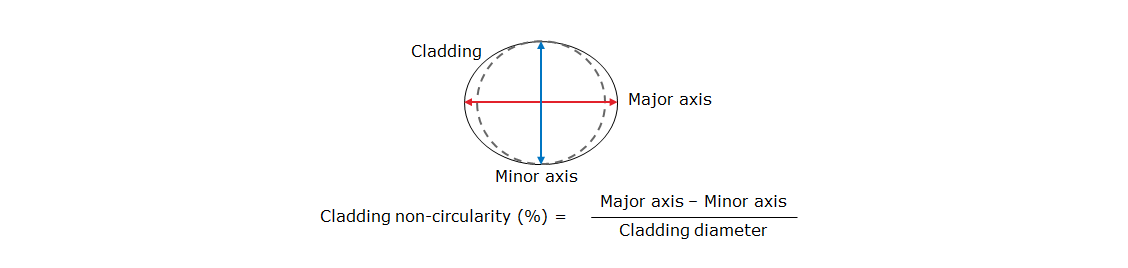
Cladding Non-Circularity
Cladding non-circularity is defined in the figure.
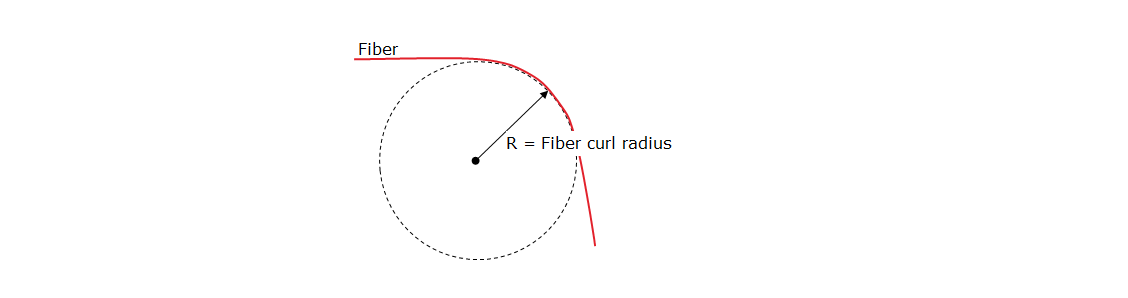
Fiber Curl Radius
Fiber curl describes a tendency of optical fiber to curve along their length when released from winding on a spool, which affects the splice quality.
Fiber curl radius is defined as the radius of curvature.
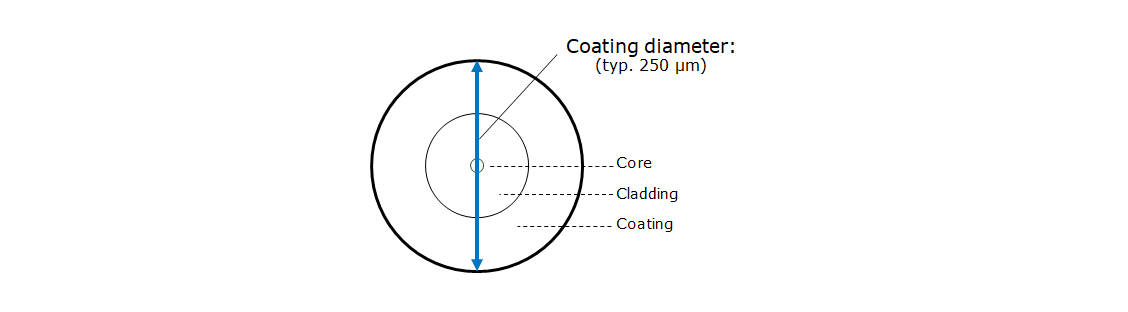
Coating Diameter
Coating diameter is the outer diameter of optical fiber’s protecting layer which is made of acrylates which is the vertical blue line in the figure.
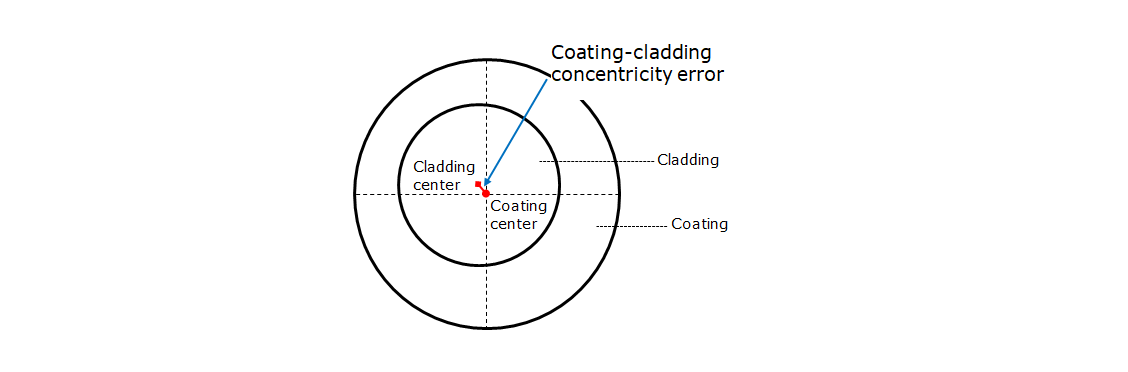
Coating-Cladding Concentricity Error
Coating-cladding concentricity error is the relative position of the cladding against the coating in an optical fiber.
Attenuation
Attenuation describes the reduction of optical signal power, and is defined as ratio of the optical power at two points, typically expressed as the logarithm of the ratio in decibel (dB).
For optical fiber, attenuation per unit length, e.g. dB per kilometer (dB/km), is typically used as the attenuation coefficient.
Lower attenuation can directly improve the optical signal ratio (OSNR) for large capacity and long distance transmission systems.
Sumitomo Electric offers ultra-low attenuation optical fibers.
Zero-Dispersion Wavelength
The wavelength at which the chromatic dispersion becomes zero. For ITU-T G.652 and G.657 fibers, zero-dispersion wavelength is within 1300-1324 nm.
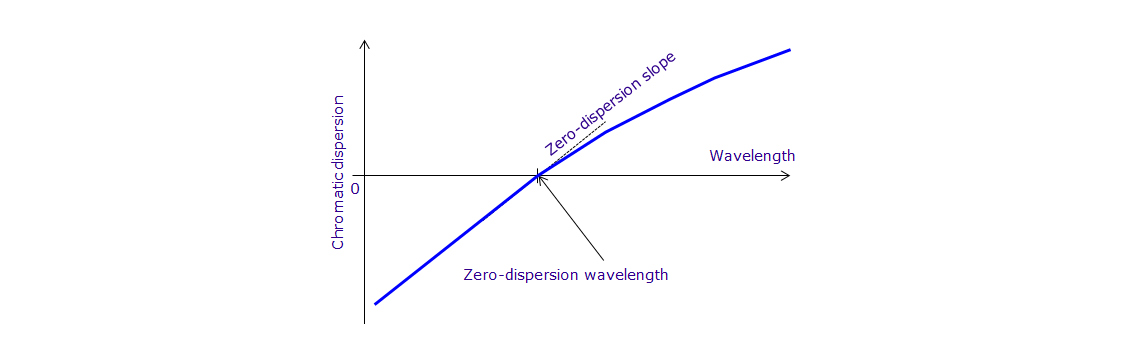
Chromatic Dispersion Slope
Slope of the chromatic dispersion versus wavelength curve.
Zero-Dispersion Slope
Zero dispersion slope is the chromatic dispersion slope at the zero dispersion wavelength.
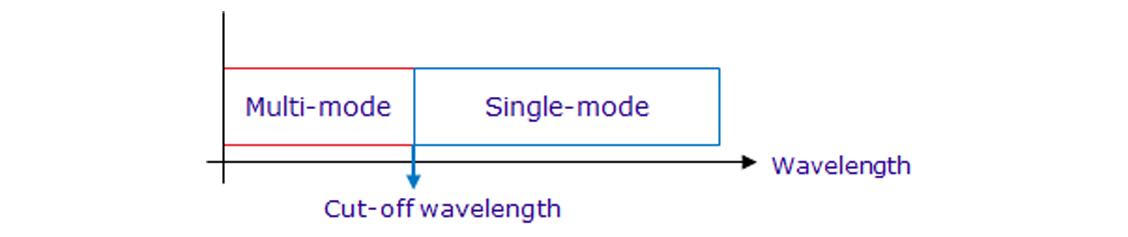
Cable Cut-off Wavelength
The cut-off wavelength of single-mode optical fiber is defined as the shortest wavelength at which only a single mode can propagate.
Two approaches can be used to determine the cut-off wavelength:
- Fiber cut-off wavelength: This is measured on a short, uncabled fiber, typically around 2 meters in length.
- Cable cut-off wavelength: This is measured on a substantially straight 22 meters cable prepared by exposing 1 meter of decabled fiber at both ends. Alternatively, cable cut-off wavelength can be measured on 22 meters of uncabled fiber loosely coiled with > 140mm radius, incorporating a 40 mm radius loop at each end.
Cable cutoff wavelength is preferred to be specified. The recommended cable cut-off wavelength is ≤1260 nm for ITU-T G.652 and G.657, while it is ≤1530 nm for ITU-T G.654.
Proof Stress Level
The proof stress level refers to the specified value of tensile stress or strain applied along the entire length of the fiber for a short period of time. Sumitomo Electric sets the proof stress level higher than international standards, such as ITU-T Recommendations and IEC Standards, to enhance the resistance of our fiber products to failure.
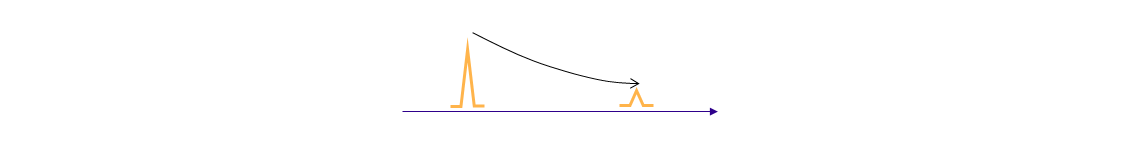
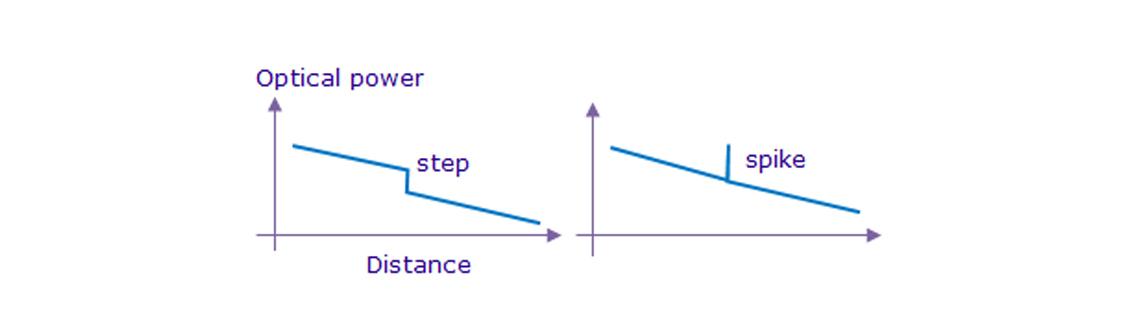
Point Discontinuity
Point discontinuity refers to local deviations on OTDR traces, such as steps or spikes (as illustrated in the following figure).
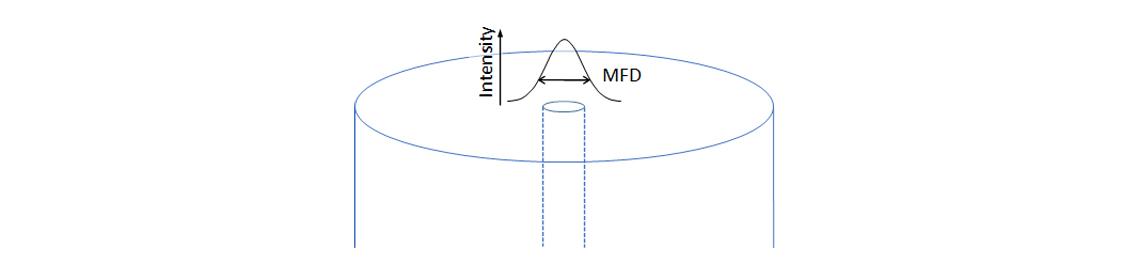
Mode Field Diameter (MFD)
Mode field diameter (MFD) is a measure of the cross-sectional area of the optical field distribution in a single mode fiber. Fibers complying with ITU-T G.654.B, D, and E have a larger MFD compared to G.652 and G.657, improving the optical signal to noise ratio (OSNR) for long distance transmission. The MFD value generally increases with longer wavelengths.
Chromatic Dispersion
An optical signal is generally propagated through a fiber in the form of a pulse. Chromatic dispersion represents the spreading of optical pulses in an optical fiber, caused by the different group velocities of the various wavelengths composing the optical signal spectrum. Chromatic dispersion coefficient is a change of group delay per unit length of fiber caused by a unit wavelength change, which is usually expressed as ps/(nm×km).
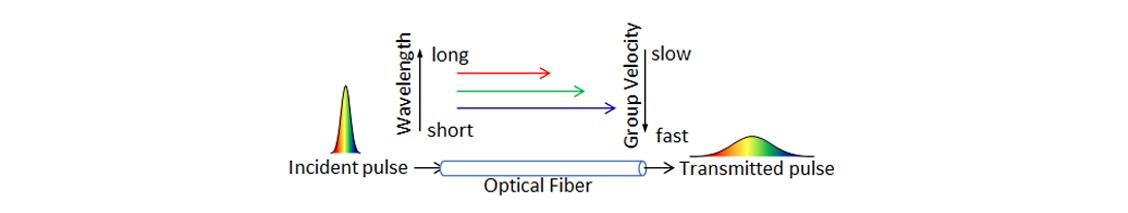
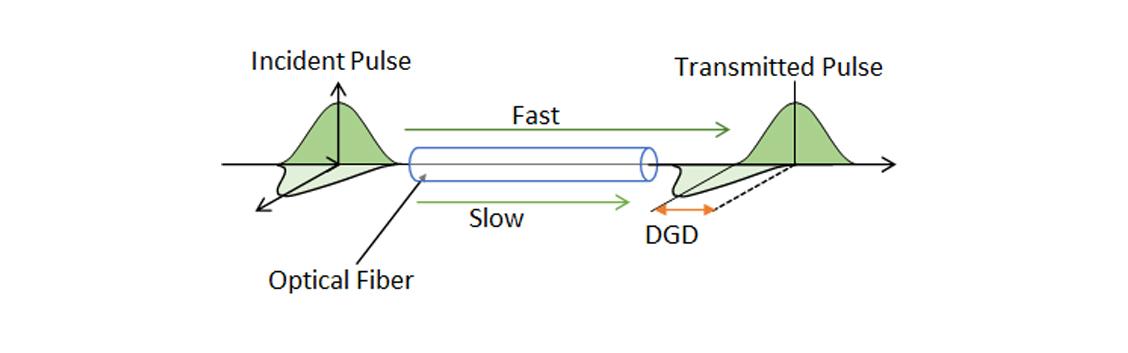
Polarization Mode Dispersion
Ideally, an optical fiber has a circular symmetric cross-section. However, a real optical fiber cannot be perfectly circular and can undergo local stresses. Consequently, the two orthogonally-polarized modes in the fiber travel at different velocities, causing a pulse broadening and signal degradation. Since the differential group delay (DGD) time between the two orthogonal modes varies randomly along the fiber and in time, Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) is defined as an average of the DGD.
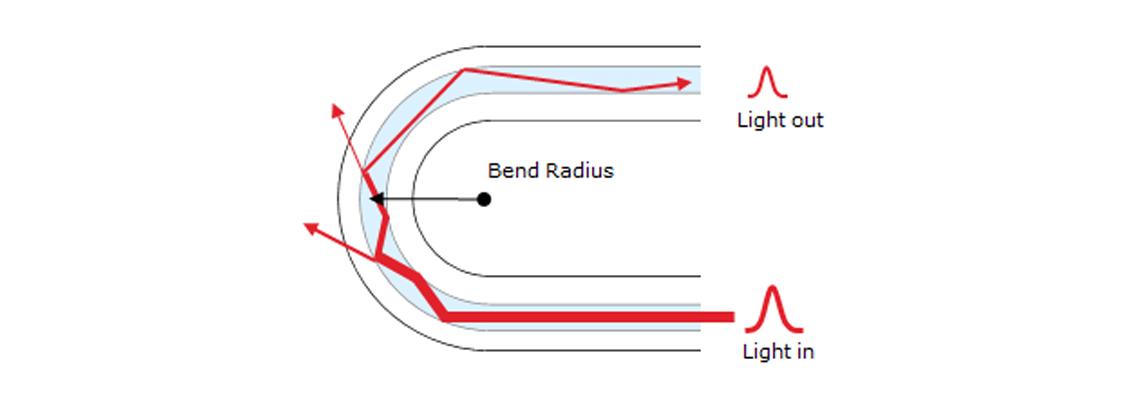
Macrobending Loss
Macrobending loss refers to attenuation of an optical signal's power due to a fiber bend. The smaller the bending radius, and/or the higher the number of windings, the higher the macrobending loss. It also generally becomes higher at longer wavelengths.
Coating Strip Force
Optical fiber is coated with protective acrylate layers. Coating strip force is the force required to mechanically remove the protective coating from the optical fiber along the longitudinal axis.
Tensile Strength
The maximum tensile stress that the optical fiber can withstand before breaking when it is axially pulled.
