Ushering in a new era for the modern world with IoT technology
Connecting everything around us
The Internet of Things, or “IoT”, refers to a network of devices (or “things”) connected to the internet that can collect and transfer data over a communication network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction. IoT offers the potential for a smarter and more responsive world and gives us all sorts of benefits that weren’t possible before. Data is automatically measured and transferred over a network to data stores by connected devices. These devices operate on embedded sensors which are used to collect and transfer data. IoT technology is utilized in a wide range of areas and industries. These include smart homes, healthcare, agriculture and manufacturing. Connected smart devices that benefit from IoT include remote baby monitoring devices, devices that allow you to remotely control various functions such as temperature and appliances in your home, and devices that allow companies to monitor their manufacturing sites and increase production efficiency.
Reducing product defects using IoT technology

In today’s world, the manufacturing industry is constantly seeking new methods and technologies that will help them increase profit margins by streamlining operations. Another major challenge for manufacturers is reducing the number and frequency of defective products. There are various causes for such defects, but they typically fall under the five basic elements of “man”, “machine”, “material”, “method” and “measurement”, and are referred to as the 5Ms of manufacturing.
By reducing product defects caused by human error, it is possible to prevent customer complaints in advance and provide a more satisfying customer experience. Connecting manufacturing devices and analyzing the collected data is enabling manufacturers to do just that. In recent years, many smart factories are starting to use technologies such as image recognition and sensing to reduce product defects. These technologies include the introduction of AI-enabled industrial robots, which can manufacture at a steady speed to improve production volume.
However, there are some pitfalls of discovering product defects using IoT. Theoretically, product defects can be reduced by using technologies such as image recognition and sensing, but on the actual manufacturing sites, this is not necessarily the case. For example, when detecting a manufactured product using image recognition, it may not be able to accurately detect it depending on the lighting condition or direction at the worksite. The technology is not yet perfect, but there is no denying its many overwhelming benefits. If early identification of failure locations and predictive detection of equipment failure becomes possible, effects such as quality improvement, efficiency of maintenance work, reduction of maintenance costs and prevention of the outflow of defective products can be expected.
IoT in Sumitomo Electric’s factories
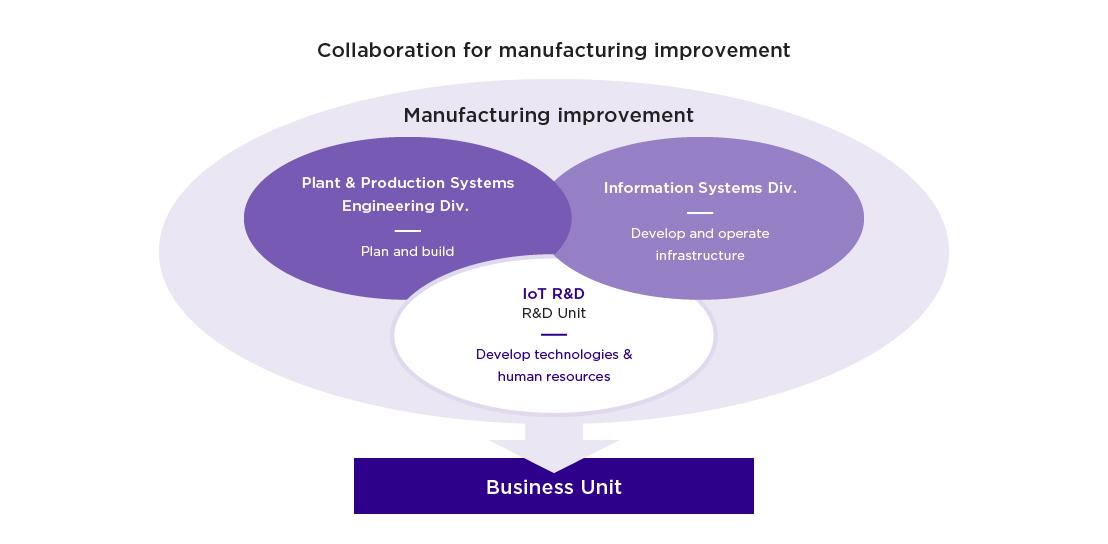
IoT technologies to collect and analyze data by connecting multiple sensors and devices to networks have been introduced increasingly into various manufacturing fields in recent years. At Sumitomo Electric, departments such as Plant&Production Systems Engineering, IoT R&D, and Information Systems work together to streamline the sharing of information between the manufacturing sites and the research department, and to improve product quality. This system comprised of these three departments is the biggest feature of IoT R&D at Sumitomo Electric.
They are pushing ahead with the development of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies such as sensing systems, wireless communication, and big data analysis using AI to support manufacturing in their group. Their focus is on productivity improvement, automated inspection, predictive maintenance and work safety. In most cases, these departments have separate bases and operate independently. But at Sumitomo Electric, staff members from the IoT research department, for example, are deeply involved on the manufacturing floor. That is why they can develop “usable IoT” that listens to the voices at the worksite in real-time, reflects them to the IoT research department and grasps the circumstances and detailed requests unique to each site.
They mainly utilize IoT technology to reduce product defects. Their main strength lies in detecting defective products using image recognition. Typically, they used sensors and image recognition technology when trying to detect product defects. However, there are many cases where clear images cannot be taken due to the condition or direction of the lighting at the actual work site. This causes them to let defective products go through without detecting them. In response, they significantly improved the detection rate of defective products at their factories. They did this by increasing the accuracy of image recognition using AI. They also customized the sensors according to each worksite, such as the placement of the camera and direction of the lighting. AI and IoT technology have become an emerging social trend. By accumulating know-how with analogue methods such as these, the accuracy of the latest technology will increase. This is a technology that has been made possible by their in-house manufacturing factory and by integrating their IoT research with the manufacturing floors.
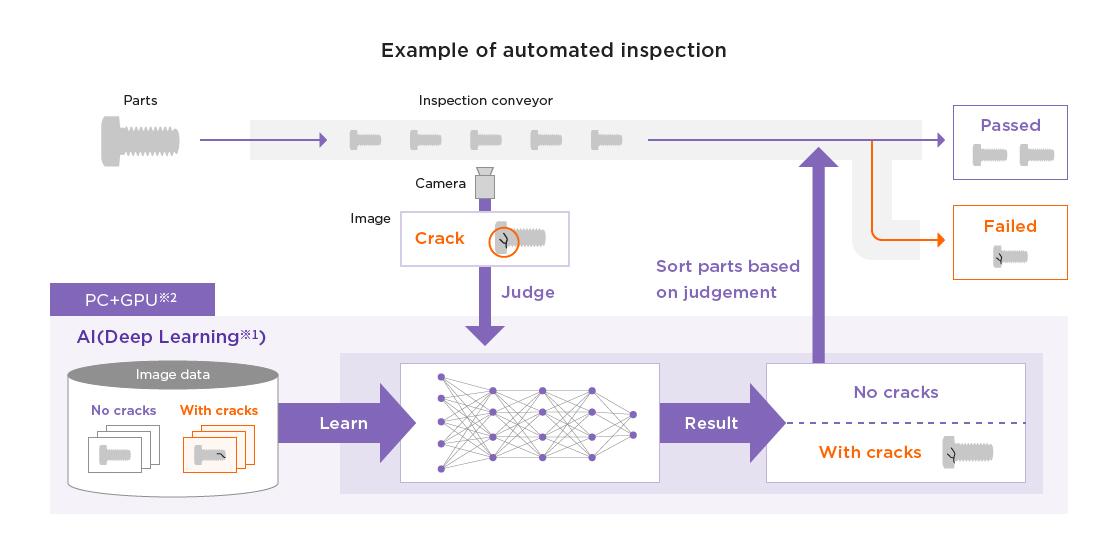
※1 Deep Learning: AI technology that performs learning by using a multilayered neural network which imitates the structure of the human brain
※2 GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): specialized processor designed for image processing
In the future, They will continue to conduct research and development to realize the ideal smart factory. They need to visualize (digitalize) the manufacturing processes from start to finish and establish a digital twin which serves as a virtual replica of what is happening on the factory floor in near-real time. By visualizing every event that takes place in the factory, it will become possible to predict future events. It will create many benefits for the factory, including the reduction of product defects, reduction of lead-time and prevention of accidents.