Registration of public notification
If you register your e-mail address, we will notify you when the latest issue is published. If you wish, please register from the registration form. To delete your registration, please visit here.
April 2024 No.98
Featured Topic: Automotive Business Toward “Sumitomo Electric Group 2030 VISION”
The automotive business of Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. has grown over a long period of time focusing on wiring harnesses . Meanwhile, the automotive industry has been facing the challenge of a once-in-a-century revolutionary transition known as CASE (connected, autonomous, shared, and electric) innovation. The transition is not expected to be limited simply to introducing these elements of connection, automation, sharing/service, and electrification. It has the potential to change the position of cars in society and considerably transform the structure of the automotive industry.
1.3 MB
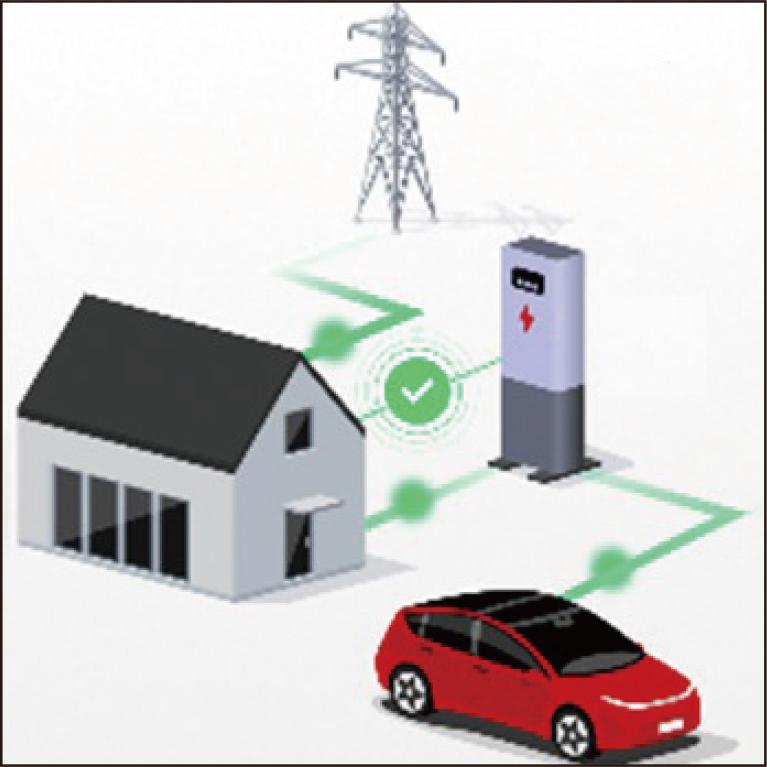
The automotive industry is currently undergoing a once-in-a-century transformation, with the global adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) playing a significant role in reducing CO2 emissions and mitigating global warming. Alongside, there is a growing need to manage power generation and load fluctuations in the power system that accompany the widespread implementation of renewable energy. In response, the Sumitomo Electric Group has made valuable contributions to society by introducing Traffic Vision Green, a mobility service product that supports comfortable EV driving, and sEMSA, an energy service product that generates optimal operation plans for distributed power sources. Looking ahead, we envision the development of efficient and cost-effective energy management systems (EMS) that consider EV operating conditions by integrating mobility and energy. This paper highlights Sumitomo Electric Group's past accomplishments and outlines our future initiatives for integrated energy management systems that merge mobility and energy sectors.
2 MB
2 MB
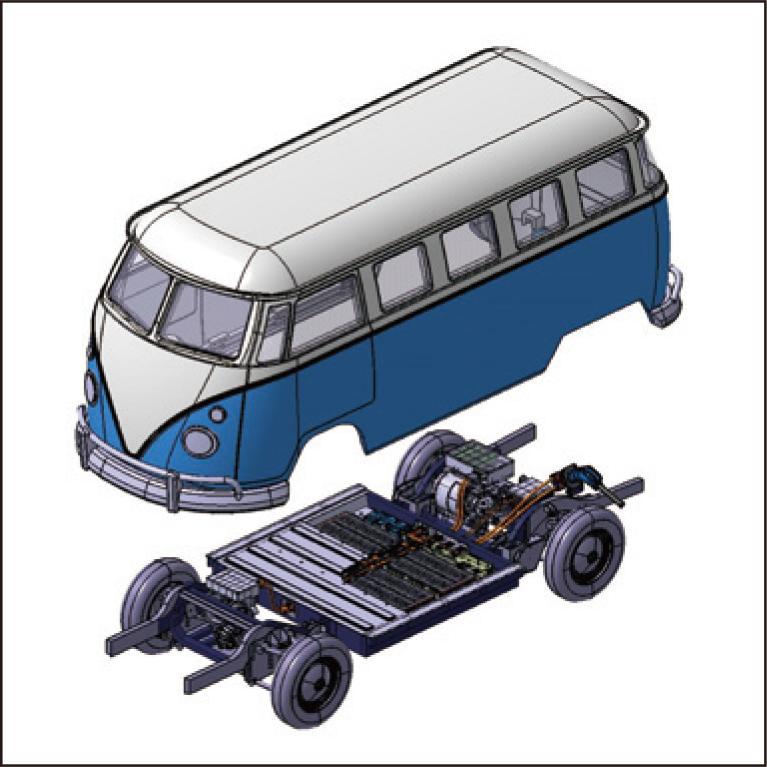
With a commitment to environmental sustainability and carbon neutrality, electrification of mobility is progressing significantly. The Sumitomo Electric Group develops and provides a wide range of key technologies and products related to electrification, with “connecting materials/technologies” as our core focus. This paper offers a comprehensive overview of our diverse portfolio, which encompasses four distinct categories: Battery Peripheral, Motor/Inverter Peripheral, High-Voltage Interconnection Wiring/Connectors, and Charging/Infrastructure.
3.2 MB

3.2 MB
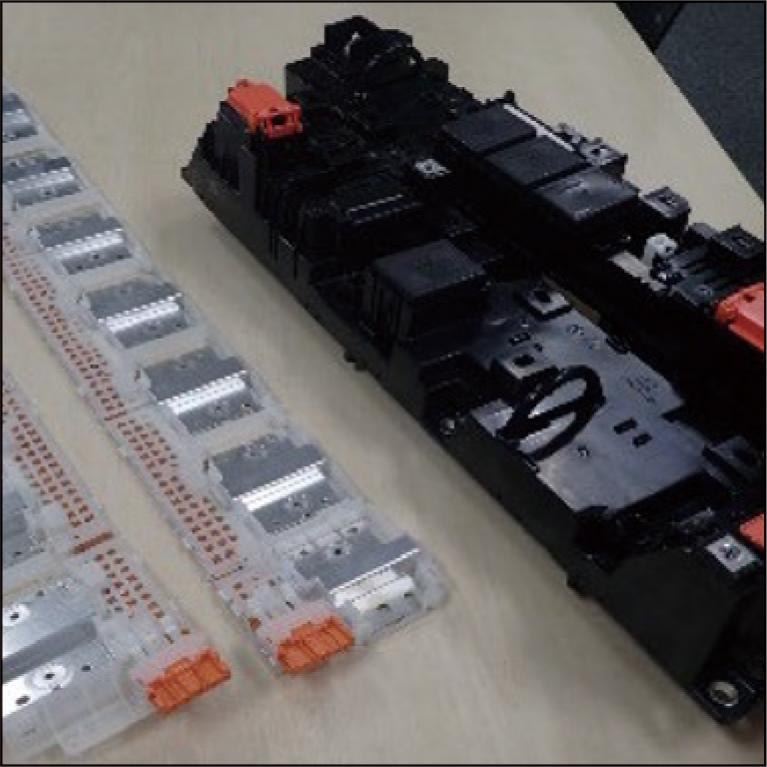
The increase in motor cars, specifically hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), plug-in hybrid electric Vehicles (PHEVs), and battery electric vehicles (BEVs), is expected to be driven by policies promoting fuel economy and CO2 emission control. In order to support the growth of BEVs, we are developing and mass-producing connection parts such as battery wiring modules, high-pressure junction boxes, and wiring harnesses for battery packs. These connection parts play a significant role in improving the performance of the battery packs by ensuring compact size, space efficiency, and high current capacity. This paper highlights the features and benefits of our battery wiring module and high-voltage junction box as essential components in the battery pack.
2.6 MB
2.6 MB
Steep surges generated by high-voltage inverter-drive motors are expected to cause significant damage on the insulators of magnet wires. Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. has developed a novel magnet wire with uniform closed microcells introduced into the insulation. This paper discusses the excellent dielectric properties of the newly developed magnet wire.
1.6 MB

1.6 MB
The automotive industry is becoming increasingly intellectualized through CASE (Connected, Autonomous, Shared, and Electric) innovations. While development times for in-vehicle systems are lengthening, products must be brought to the market quickly to remain competitive. We are making efforts to utilize digital engineering for design verification of in-vehicle systems in order to derive optimal architectures in a short period. We have applied mathematical optimization to the verification flow of the system architectures with the number of zone ECUs and the number of variations as parameters. This paper presents our efforts to shorten the verification time by combining the derived results with the response surface method, which predicts optimal conditions for the design parameters.
1.7 MB
1.7 MB
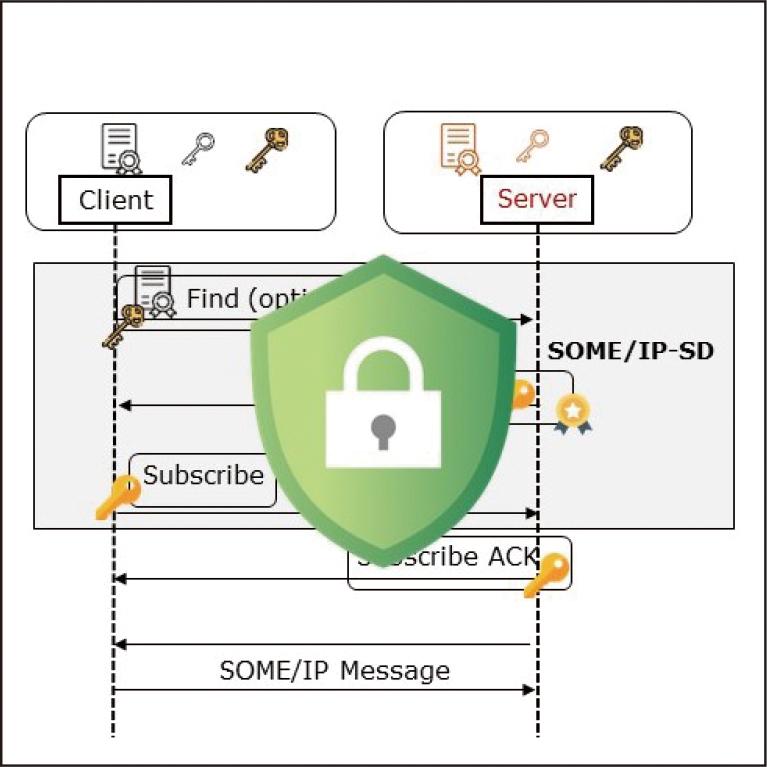
Ethernet and SOME/IP (Scalable service-Oriented MiddlewarE over IP) have been increasingly applied to modern vehicles. Although SOME/IP serves as an automotive middleware solution for control message transmission, it lacks security measures, making it vulnerable to various attacks. To address this issue, we present a security extension protocol for automotive Ethernet. Furthermore, we evaluate the protocol and demonstrate its effectiveness.
1.1 MB
1.1 MB
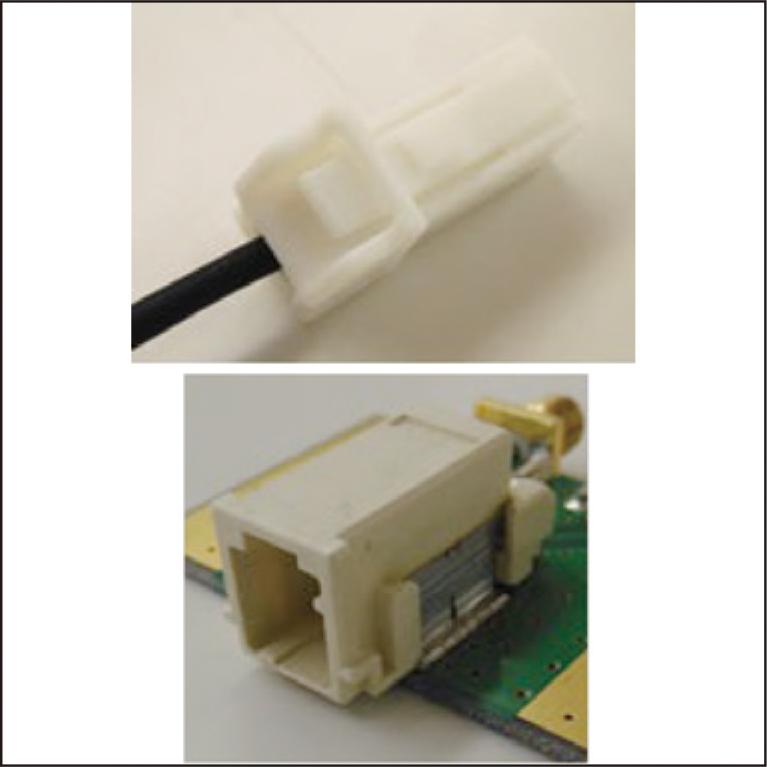
Driven by evolutions in CASE (connected, autonomous, shared & service, and electric) technology, the need for fast in-vehicle networks has increased, making in-vehicle Ethernet an attractive next-generation communication solution. To comply with the strict communication standards set by the standards organization OPEN Alliance, our focus turned to investigating 100 M Ethernet compatibility. Initial evaluation using existing CAN components revealed disparities in transmission and crosstalk characteristics of wires and connectors. Therefore, we have developed new wires and connectors, as well as terminal processing technology, CAE analysis technology, and communication characteristic evaluation technology, all of which are necessary for the development of high-speed communication components. These efforts ensured compliance with the communication standards. We view high-speed communication components as vital elements of wiring harnesses, and are committed to their ongoing development, recognizing the significance in facilitating efficient in-vehicle communication.
4.9 MB
4.9 MB
With the advancement of CASE technologies, particularly automated driving, the demand for high-volume information processing devices like LiDAR is increasing, necessitating faster in-vehicle data communication. Sumitomo (SEI) Electronic Wire, Inc. is actively engaged in developing and manufacturing information transmission sub-harnesses that comply with new global communication standards to enable high-capacity data communication. Additionally, the company has developed automated processing equipment for the efficient production of widely used connectors in sub-harness processing. This paper provides an overview of in-vehicle equipment trends, communication standards, and our wire and terminal processing technology, which are integral to high-speed communication sub-harnesses that connect these devices.
2.6 MB
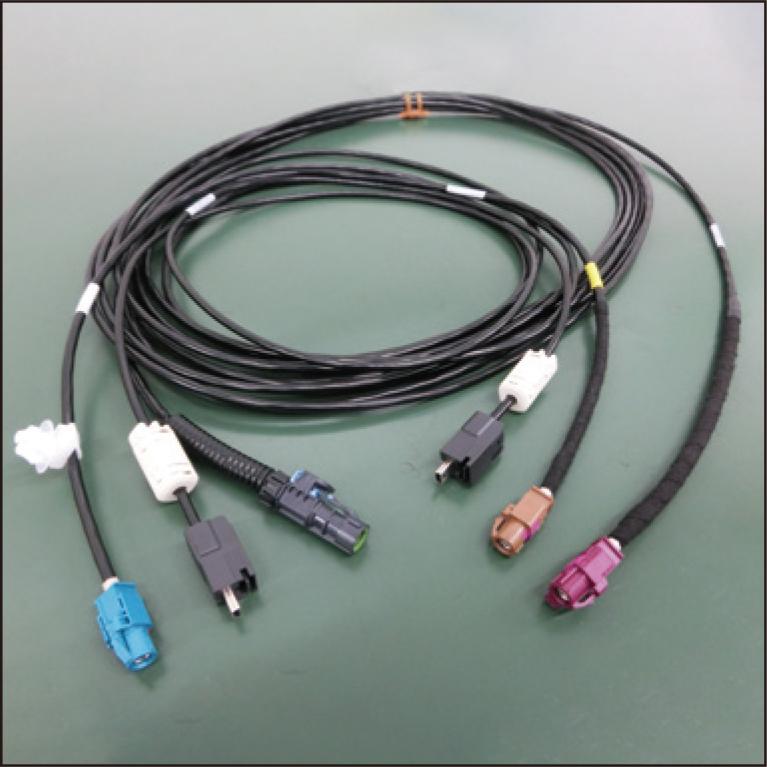

2.6 MB
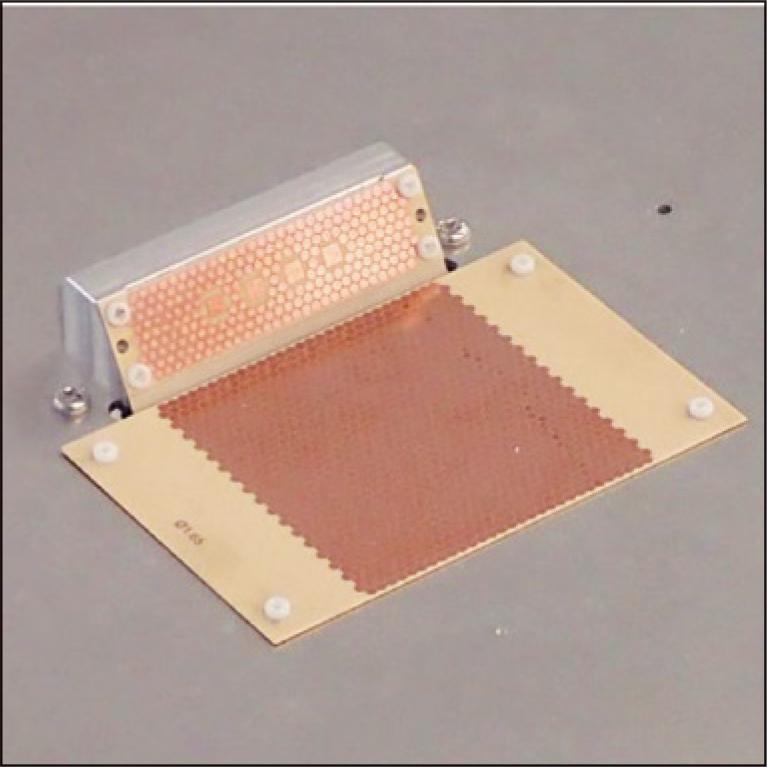
This paper reports on the development of an antenna suitable for 5G millimeter wave (mmWave) communication, incorporating metamaterial technologies such as Electromagnetic Band Gap (EBG) and Artificial Magnetic Conductor (AMC). The goal is to achieve automated driving by utilizing 5G, which offers high-speed, large-capacity, and low-latency features. To enable efficient data communication, particularly for sensing information, the use of mmWave band with a bandwidth of several hundred MHz is required. However, the use of an array antenna consisting of multiple patch antenna elements on the roof of a vehicle poses challenges in terms of radiation characteristics. This study aims to address these challenges through the development of an antenna suitable for 5G mmWave communication.
2.7 MB
2.7 MB
The spread of autonomous driving and the movement toward CASE (connected, autonomous, shared & service, electric) vehicles has led to an increase in the number of devices and electrical circuits in automobiles. However, in order to improve comfort, there is a need to increase the interior space of vehicles, which requires a change in the wiring harness design to fit into smaller and tighter spaces. Meanwhile, the complex nature of wiring harness manufacturing makes it difficult to automate, resulting in a manual-intensive process that requires a large number of workers across global locations. This presents challenges in terms of cost and carbon emissions associated with long-distance shipping to OEM factories. To address these challenges, we have developed e-STEALTH W/H, a new wiring harness that not only increases interior space in vehicles but also enables automation, shifting from labor-intensive processes to localized production for local consumption. The successful adoption of our wiring harness by a major automaker underscores its effectiveness. This paper outlines the structure and key technologies of e-STEALTH W/H and provides insights into our innovative wiring harness solution.
2.2 MB
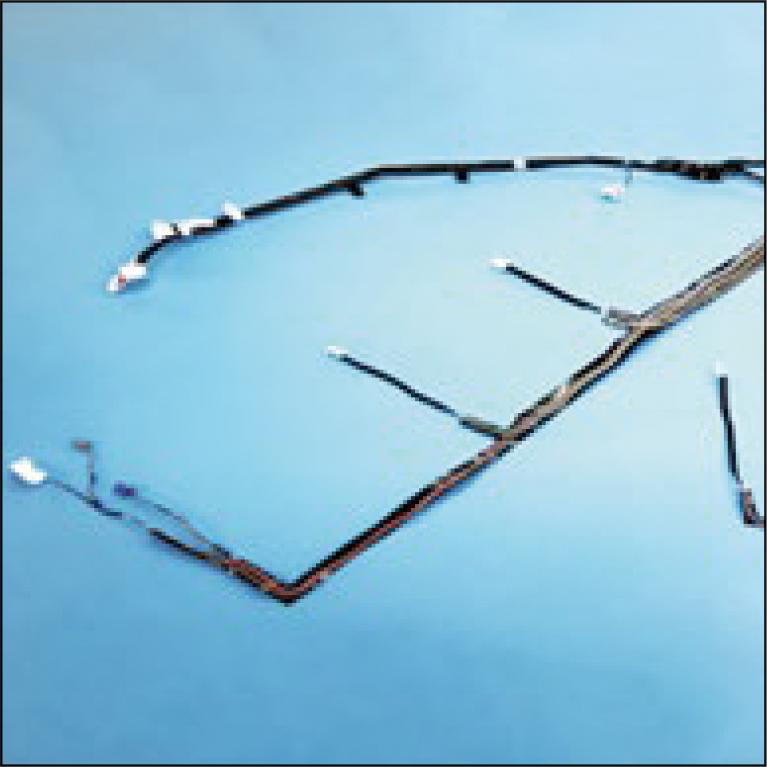

2.2 MB
In the automotive industry, with the goal of reducing CO2 emissions by improving fuel efficiency, there is a need for high-performance aluminum materials that can contribute to reducing the weight of automotive components. We have been working to improve the strength and heat resistance of aluminum alloys for forged automotive components. By improving the alloy composition and processing methods, we have developed two aluminum alloy wires with higher strength and higher heat resistance than widely used 6000 series aluminum alloys. This paper introduces the development of the aluminum alloy wires and the characteristics of the developed aluminum alloys.
2.1 MB

2.1 MB
The growing emphasis on mitigating global warming has highlighted the need for sustainable solutions in the e-mobility sector. In response, the automotive industry requires traction motors that deliver increased speed, torque, and efficiency. Through the integration of advanced technologies in stator magnet wire and slot cooling, we have successfully developed a downsized stator architecture for traction motors. This innovative design concept maintains maximum torque while achieving significant size reduction. Furthermore, the production process for this stator contributes to a reduction in CO2 emissions by approximately 30%, compared to conventional stators.
1.8 MB
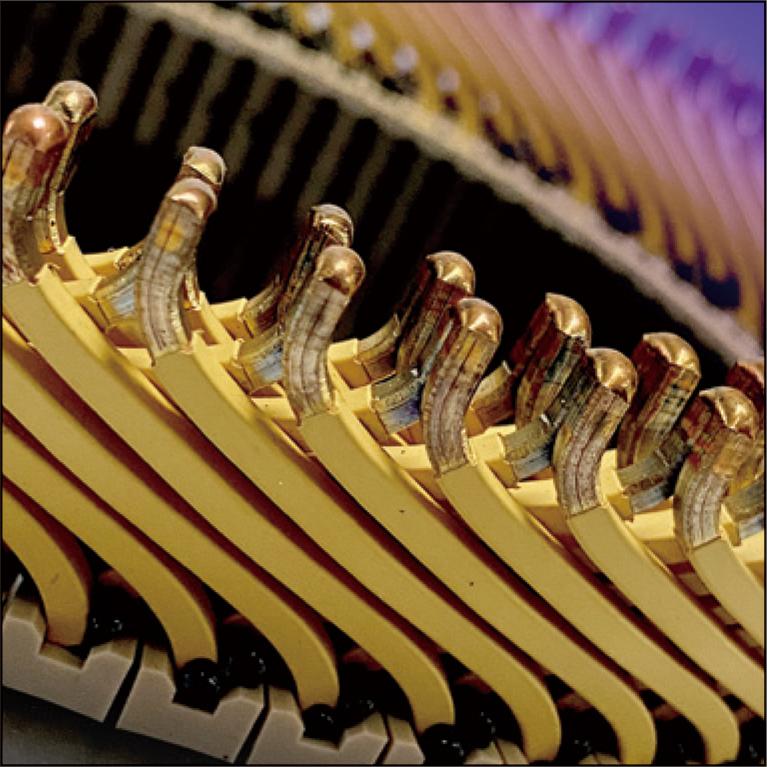

1.8 MB
As the electrification of automobiles progresses, the number of parts used in rolling and sliding environments, such as gears and bearings, which are often used in motors and reducers, is increasing. Therefore, improving their durability and reducing their friction loss are considered to be important. We coat various diamond like carbon (DLC) depending on the application. Among them, it has been confirmed that hydrogen-free DLC has a high friction reduction effect in lubricating oil. In this study, we investigated changes in durability when applying hydrogen-free DLC to gears and the friction reduction effect of hydrogen-free DLC in rolling and sliding environments. As a result, it was confirmed that coated gears with hydrogen-free DLC improve their durability. It was also confirmed that the friction reduction effect of hydrogen-free DLC is higher in environments with “lower viscosity of oil,” “higher rotation speed,” and “higher slip ratio.”
2.2 MB
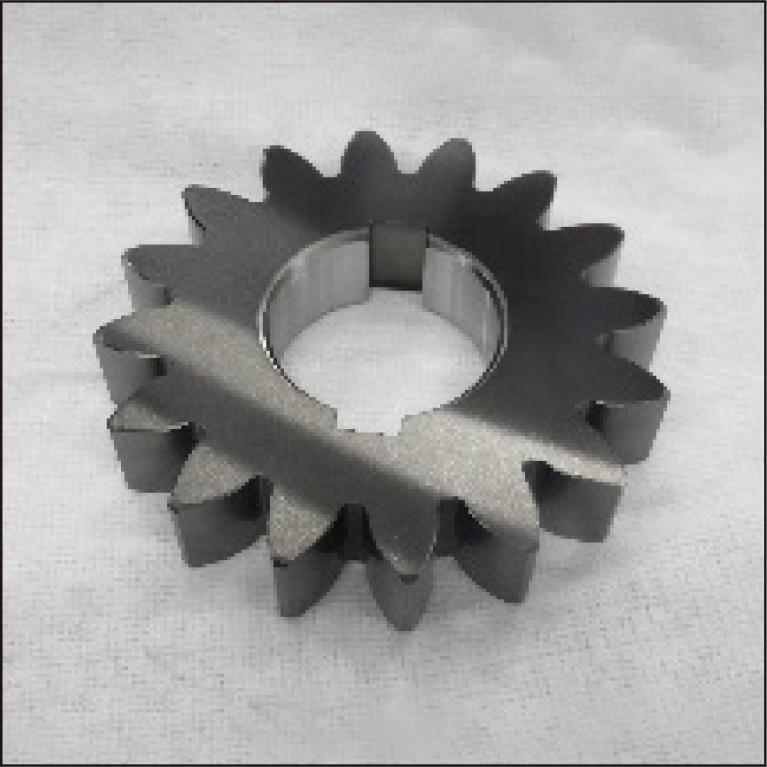

2.2 MB
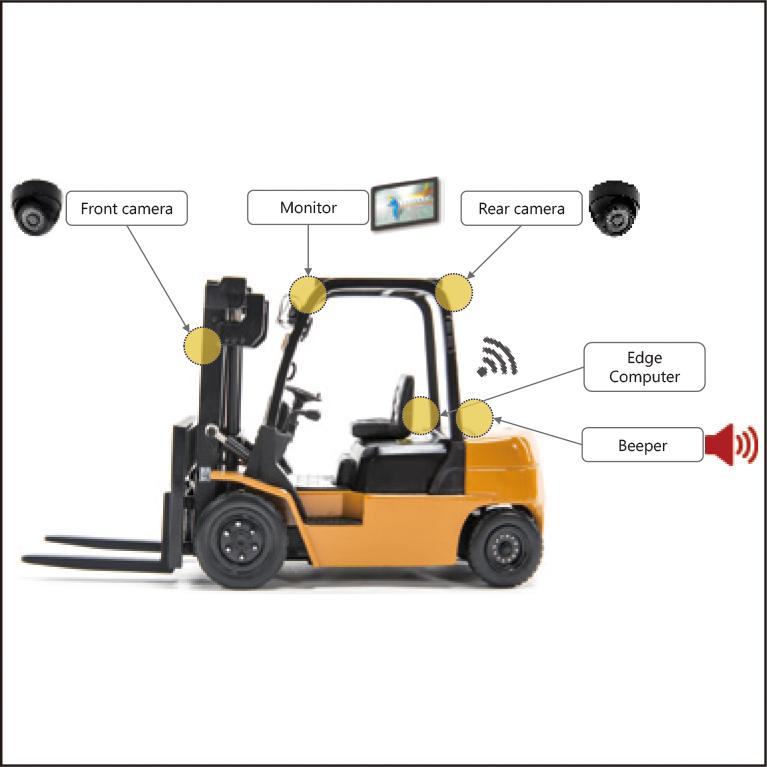
To mitigate accidents involving forklifts and people, we have developed a forklift safety support system capable of detecting the presence of people near a forklift. Real-time responsiveness is crucial, necessitating immediate detection and reporting. To address this, we propose utilizing edge computing to enable swift responses. This paper introduces a forklift safety support system leveraging edge AI installed in a compact edge computer. Additionally, we discuss the evaluation of edge AI's accuracy and speed at the edge, along with the examination of techniques to enhance the accuracy efficiently.
2.8 MB
2.8 MB
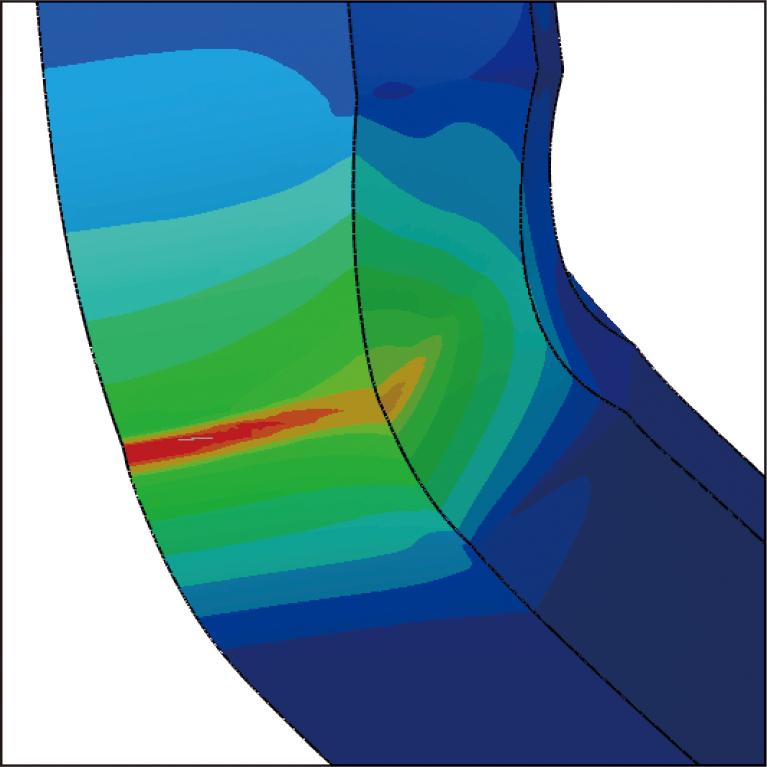
As terminals for automotive connectors become smaller, the copper alloys used for the terminals are becoming thinner and stronger. Terminals are formed mainly by bending, but the higher strength of copper alloys makes bending cracks more likely to occur. In the past, this problem was handled by trial and error based on experience, but in order to cope with the recent short development period, a technique for predicting bending cracks using CAE is required. Although special elasto-plastic analysis reflecting the crystallinity of metals has been reported as a conventional prediction technique for bending cracks, it has been difficult to apply this technique to actual copper alloys for terminals. Therefore, based on the occurrence mechanism of bending cracks, we considered that shear deformation resistance in the thickness direction has a significant influence on the occurrence of bending cracks, and developed a shear test method for thin sheets in the thickness direction. Based on the measurement results, it becomes possible to predict the occurrence of bending cracks by simulating bending cracks using the general elasto-plastic analysis.
1.9 MB
1.9 MB
Communication frequency in telecommunications has been increasing to improve data transmission speed and capacity. However, this increase also raises the possibility of unintentional radiated emissions from communication cables, leading to electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) problems. From the viewpoint of radiation, we examined the transmission and radiation characteristics of unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable commonly used in local area networks and in-vehicle communication networks. The examination confirmed that the UTP cable emits a portion of the transmitting signal within a certain frequency band. This emission follows the same mechanism as a leaky cable. We verified that the equation derived from the leaky cable mechanism can explain the relationship between the radiation bandwidth and the radiation angle. This paper introduces the radiated emission from UTP cable and explains the radiation mechanism in detail. Additionally, we provide a guideline on how to avoid potential EMC problem related to UTP cable.
2.7 MB
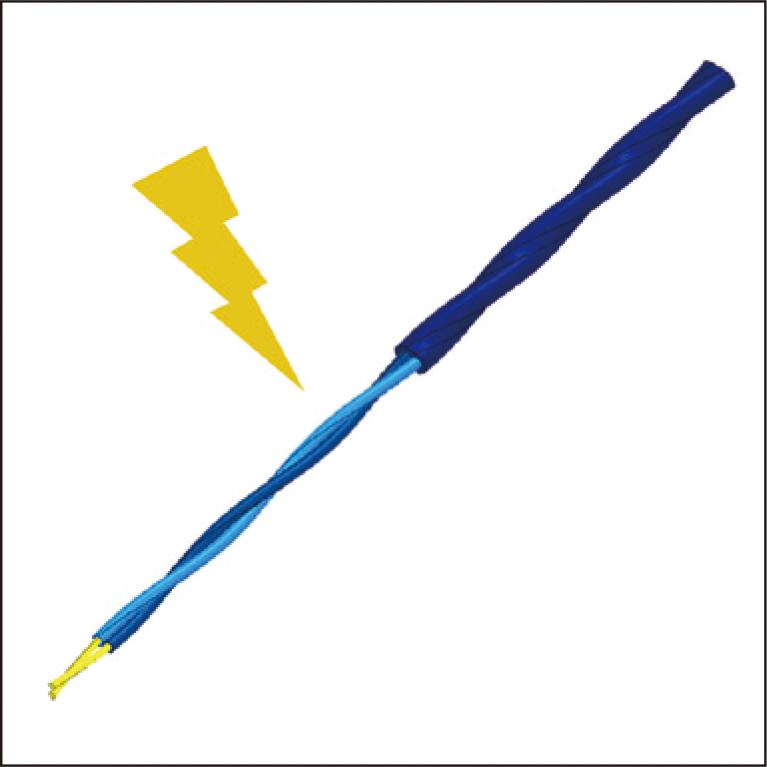

2.7 MB
Thinner optical cables are required for data center networks to meet the increasing demand of communication traffic. For these cables thinner optical fibers are essential, and one of the concerns in reducing the optical fiber diameter is the increase in attenuation by microbending in the cabling process. It is necessary to adjust the optical fiber structure based on an analytical formula that systematically estimates the effects of structural parameters. Based on Cocchini's established method for conventional optical fibers with a coating diameter of 250 μm, we have derived an analytical formula to accurately predict the microbending attenuation of optical fibers with a smaller diameter of 165 μm or less.
1.5 MB
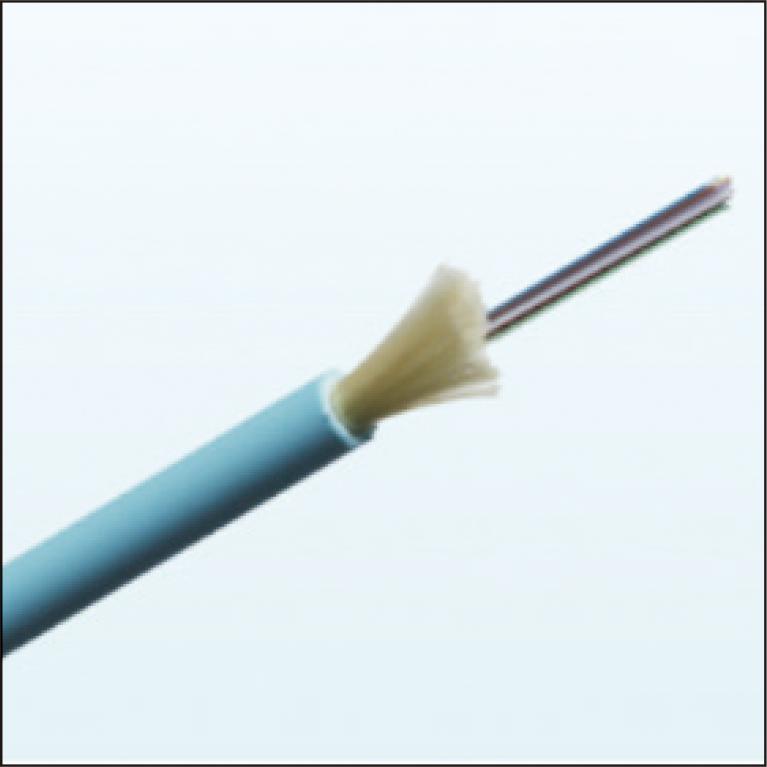
1.5 MB
With the increasing amount of internet traffic, there is a growing demand for high-capacity optical fiber communication not only for long-haul communication but also for inter-data centers communication. We have been developing InP modulators and driver ICs. Recently, we have developed a modulator module and successfully demonstrated 1 Tbit/s fiber transmission with a low power consumption of less than 3 W. We have also developed a spot size converter using 3D printing technology and achieved a low loss of 9.5 dB as part of the modulator module, confirming its reliability for Telcordia standards.
2.6 MB
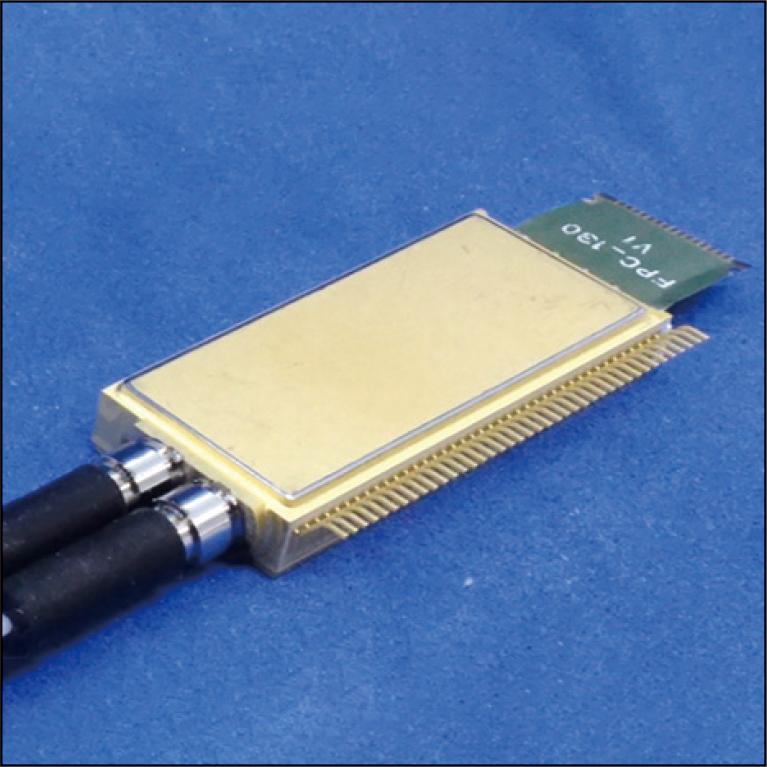
2.6 MB
This paper reports on the characteristics of a thermopile infrared sensor using nanostructured Si-Ge thermoelectric materials. While thermopile infrared sensors have the advantage of operating without power consumption, they have low sensitivity. To address this limitation, we have developed nanostructured Si-Ge thermoelectric materials that are expected to have a low thermal conductivity and a high Seebeck coefficient. With a thermal conductivity of 1/8 (0.8 W/(m·K)) and a Seebeck coefficient 2.8 times higher (330 μV/K) than that of conventional Si-Ge crystals, the nanostructured Si-Ge thermoelectric materials are expected to enhance the sensitivity of the thermopile infrared sensor. The thermopile infrared sensor using these materials achieved a sensitivity of 1,200 V/W at pressures below 1×10-1 Pa, demonstrating high sensitivity.
1.6 MB

1.6 MB
The Wi-SUN FAN (Wireless Smart Utility Network for Field Area Network profile) was initiated in 2012 as an international wireless communication standard for next-generation smart meters. The certification process for the new specification, Wi-SUN FAN 1.1, which includes improvements in communication speed, distance, and low power consumption, is expected to launch in 2024. This paper highlights the features of Wi-SUN FAN in relation to its compatibility with smart cities and provides an overview of our efforts in this field.
5.1 MB

5.1 MB
We have successfully developed a forced air-cooled 150 kW isolated bidirectional DC–DC converter, aiming to achieve a power density of 2 kW/L, equivalent to a water-cooled system. This was achieved by improving the cooling performance of the transformer, a major component, integrating the cooler for the power semiconductor and transformer, reducing the switching loss of the power semiconductor, and implementing a novel control system that minimizes the overall loss. These efforts have led to the miniaturization of our converter, comparable to our water-cooled isolated bidirectional DC-DC converter.
2.7 MB
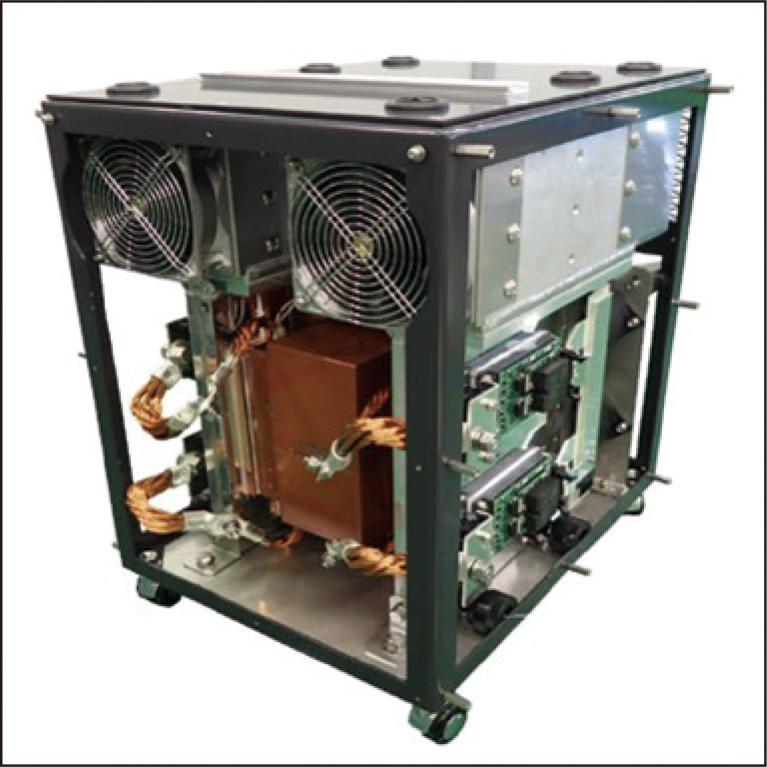

2.7 MB
In response to the tightening international environmental regulations such as carbon neutrality and CO2 emission reduction, the importance of thermal management has been emphasized in electronic products and automotive electrified products, where heat generation density is increasing year by year. In addition to the cooling mechanisms such as air cooling and water cooling, which have been the mainstream so far, there is an anticipated expansion of cooling mechanisms with excellent heat dissipation capabilities, such as heat pumps, vapor chambers, and heat storage systems. The effectiveness of these systems largely depends on the capabilities of heat exchangers and heat storage devices. To enhance their performance, we have developed porous metal materials that have both high thermal conductivity, high porosity, and micropore size. These materials can contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions by reducing the energy required for cooling.
2.4 MB
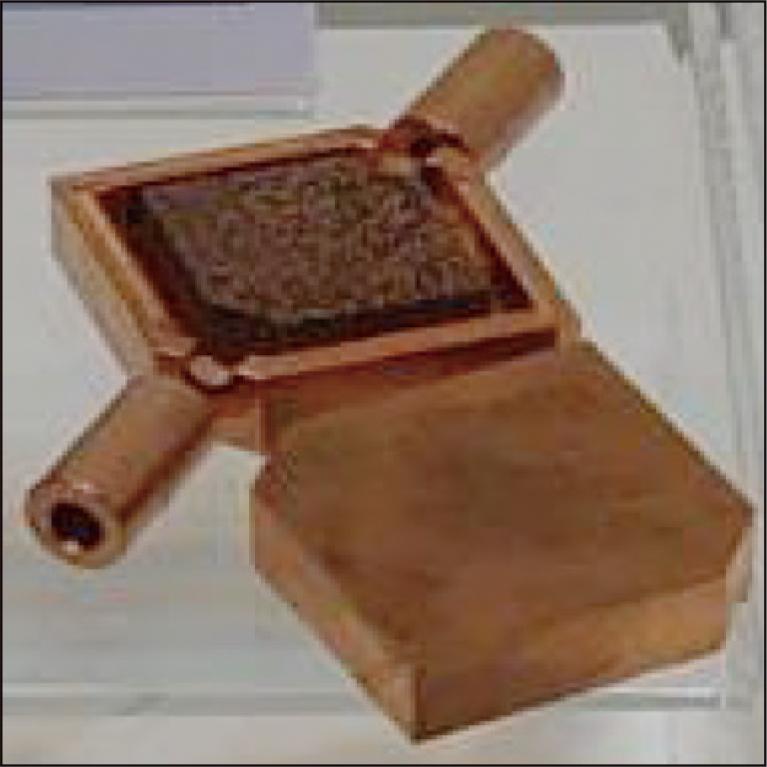

2.4 MB
We have developed a portable measuring instrument that uses diamond nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers. It operates on the USB 3.0 power supply of a laptop computer, consuming only 3 W of power. We use high-quality diamonds produced by Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. and NHV Corporation's electron beam processing to create a sensitive NV center. The device's portability is achieved through low power consumption in both the optics and the microwave source. This is made possible by a diamond corner cube that increases the photocurrent by 2.1 times compared to planar diamonds and a microwave resonator using a λ/4 transformer and a λ/4 open stub that reduces the power by 20 dB. The sensor head is compact, measuring 5 × 10 × 20 mm, and allows for magnetic field and temperature measurements. The successful implementation of these features contributes to the use of diamond sensors in various applications.
2.9 MB
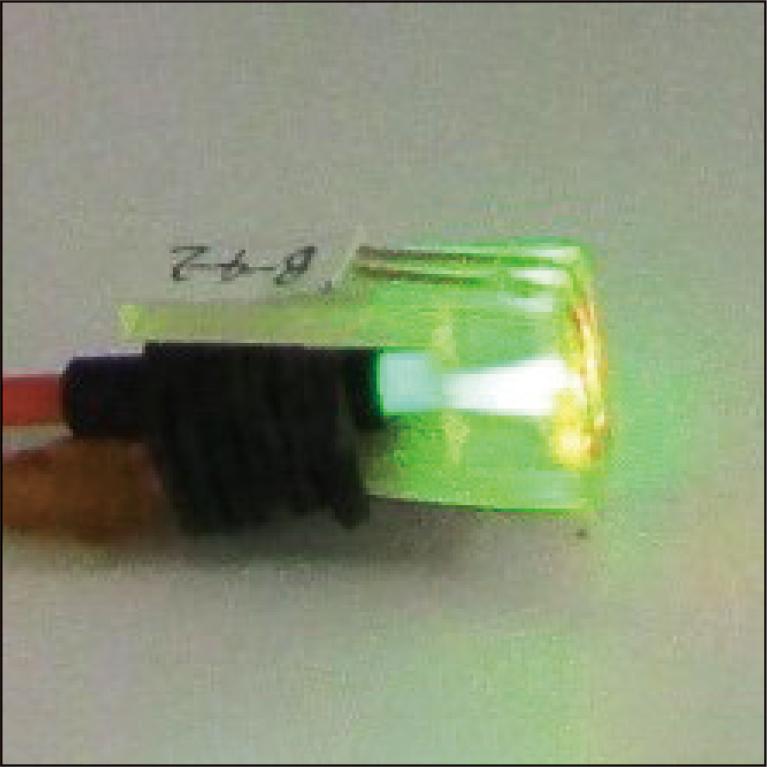
2.9 MB
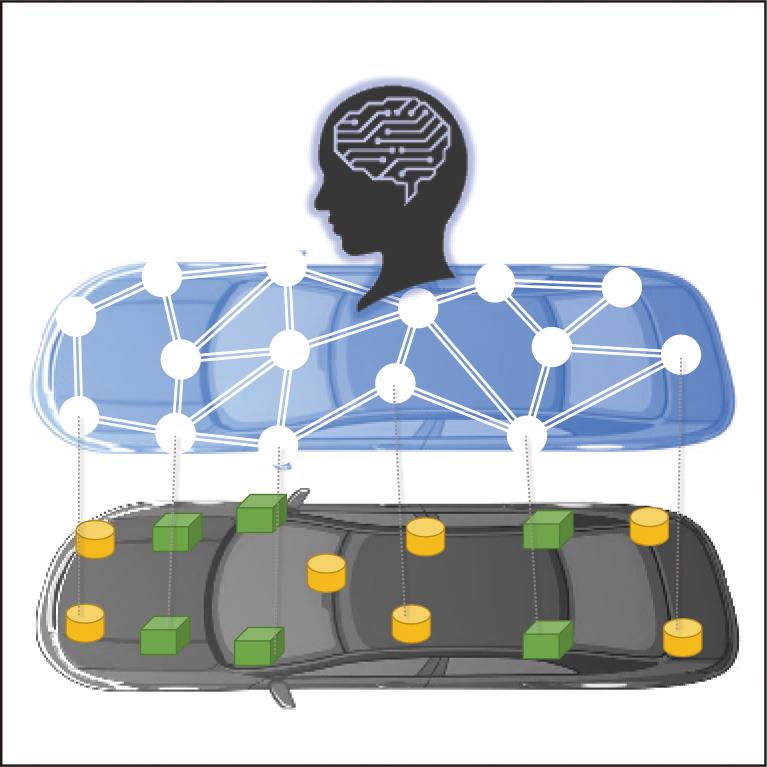
In the architecture of automotive electronic devices, functions have been conventionally implemented with discrete ECUs. The trend in these functions in the next-generation architecture, which is required to meet the needs for expandability and flexibility, is toward divided implementation into a brain (central ECU) in which control functions are integrated, and hands and feet (zone ECUs) that drive sensors and loads.
0.8 MB
Traffic signal control helps improve traffic safety, mitigate congestion, and reduce CO2 emissions by appropriately determining the green light duration and other signal control parameters suitable for traffic condition of each direction at intersections. Conventionally, vehicle detectors have been used to know the traffic conditions. However, the cost incurred by their installation and maintenance has emerged as a challenge.
0.5 MB
In recent years, communication traffic has increased rapidly due to progress in cloud computing, video streaming services, and support for 5G. Therefore, large data centers (DCs) are currently being built. Optic cables connecting DCs are mostly installed in a duct. There are instances where micro-duct optic cables are used, being suitable for the installation method that pushes the cable into the duct by feeding high-pressure air (air-blowing method). Because the interiors of DCs are required to be flame retardant, there is a need for a connection point connecting to a non-flame-retardant optic cable used outside the DC. Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. has developed and launched a 288-fiber flame-retardant microduct optic cable, which can be used inside and also outside DCs for continuous installation without a connection point.
1 MB
Our Poreflon porous materials made from stretched polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are used in various industrial fields. For example, in semiconductor-related applications, higher cleanliness levels are required for process chemical liquids due to ever-higher integration. There has been a growing need for separation membranes with smaller pore diameters. To meet the need, we have developed Poreflon nano, proprietary PTFE membranes with nano-pores. This paper describes the specifications and applications of the new filtration module, which houses Poreflon nano in an all-fluororesin package.
0.9 MB
In the field of cutting small parts—small-diameter and precision parts—used in industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical parts, there is a growing need for tools that can reduce burrs, chattering, and poorly machined surfaces and improve the quality of machining. To meet this need, Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. has developed the SL Type, which is a G-class three-dimensional (3D) chip breaker for small lathes that achieves high machining quality due to its superb sharpness. This article describes its features and performance.
3 MB
The silicon carbide (SiC) power device market is growing each year due to the rapid proliferation of electric vehicles and photovoltaic power generation systems. Accordingly, there is an upward capital investment trend, such as planned increases in production volume by a factor of two to five within a couple of years. Meanwhile, there is a trend towards the development and commercialization of 8-inch (200 mm) SiC wafers, with 6-inch (150 mm) SiC wafers currently being the mainstream. Technology development is actively underway to manufacture SiC power devices at a reduced cost.
0.6 MB
Semiconductor lasers offer better features than existing laser beam sources, being smaller in size and achieving higher efficiency and a longer service life. Their applications in society are advancing in many fields such as health care, sensing, and sheet-metal working. Moreover, they are drawing great attention from the perspective of carbon neutrality.
1.1 MB
Copyright of the paper contained in SUMITOMO ELECTRIC TECHNICAL REVIEW belongs to Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.
The paper is to be used solely for private, reference purpose, and reproduction without the permission of the copyright holder is prohibited.
Meet the Authors of the SUMITOMO ELECTRIC TECHNICAL REVIEW
We at Sumitomo Electric Group are driven to pursue technological innovations to create value for a better world.
Learn more
