Registration of public notification
If you register your e-mail address, we will notify you when the latest issue is published. If you wish, please register from the registration form. To delete your registration, please visit here.
April 2023 No.96
Featured Topic: Evolution of Information and Communication Technology and Our Roles in It
2.2 MB
In the 5th generation mobile fronthaul (5G-MFH), a wavelength-division-multiplexing (WDM) optical-transmission device is used to efficiently connect many remote units with fewer optical fibers. WDM optical-transmission device for 5G-MFH is required to meet technical requirements such as long-distance transmission and multi-rate operation at low cost. This paper demonstrates a proof-of-concept of WDM optical-transmission device supporting 10/25 Gbps multi-rate operation using signal-compensated optical transceivers equipped with a 10-Gbps-class-bandwidth optical receiver.
1.8 MB
1.8 MB
Mobile networks are shifting to the fifth-generation mobile communication system (5G) to address the need for increasing data traffic associated with the spread of high-performance mobile terminals and the diversification of services provided. 25 Gbps optical transceivers are used in 5G mobile fronthaul, and wavelength division multiplexing is widely used to expand transmission capacity. We have developed a new optical receiver that can be integrated into a 25 Gbps DWDM transceiver by combining our CAN-type optical receiver and edge-illuminated waveguide APD chip for C-Band. This paper presents the design and performance of the new optical receiver.
2.1 MB
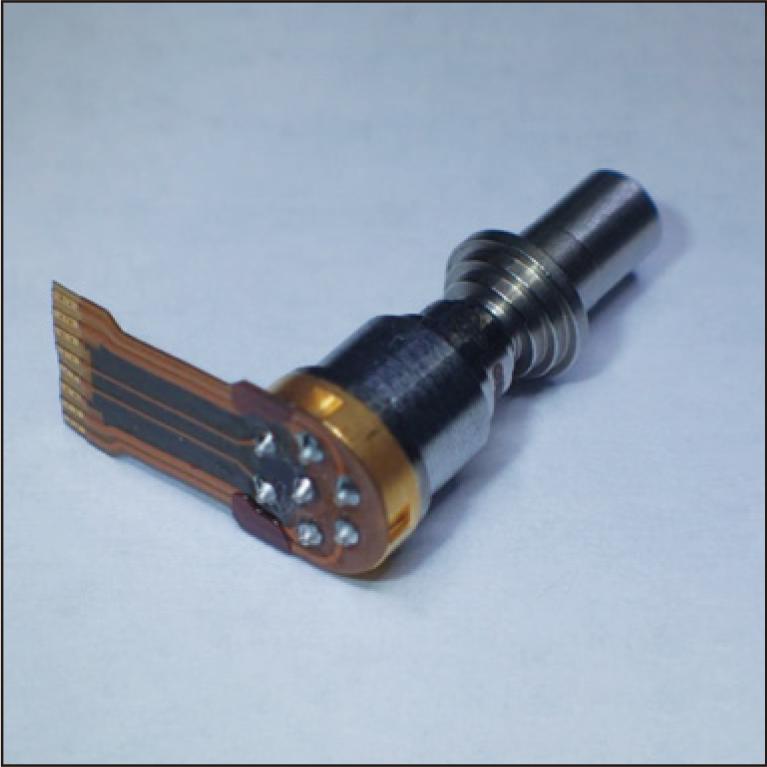

2.1 MB
The development of various IoT applications is accelerating data traffic, and it is anticipated that a data rate of more than 10 Tb/s will be required by 2030. On the other hand, conventional single-material photonic device technologies seem to have limitations to achieve both high-speed operation and low power consumption for 10 Tb/s-class data transmission. To overcome this challenge, heterogeneous integration, which combines the advantages of III-V compound semiconductors for high-speed and high-efficiency operation and Si photonics for high-density integration through device miniaturization, is expected as one of the promising approaches. This paper reports wavelength tunable lasers using heterogeneous integration.
7.8 MB
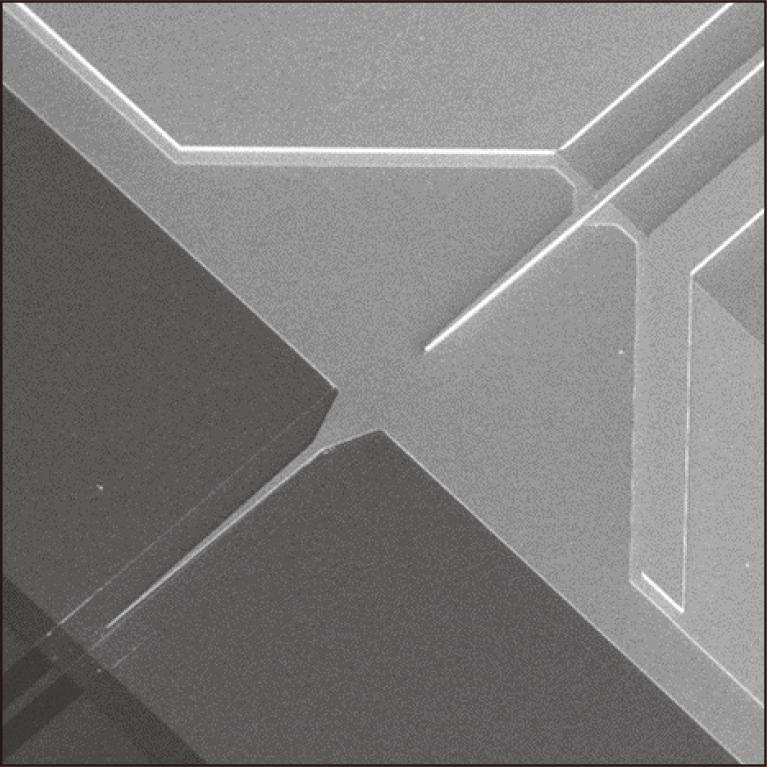
7.8 MB
To cope with the rapid increase in data traffic, 400 Gbit/s optical transceivers have been introduced in data center optical communication systems, requiring high-performance electro-absorption modulator integrated lasers (EMLs). We have developed four EMLs with center wavelengths of 1271, 1291, 1311, and 1331 nm, which meet the specifications for 400 Gbit/s optical transceivers. This paper describes the design and typical characteristics of these new EMLs.
2.8 MB
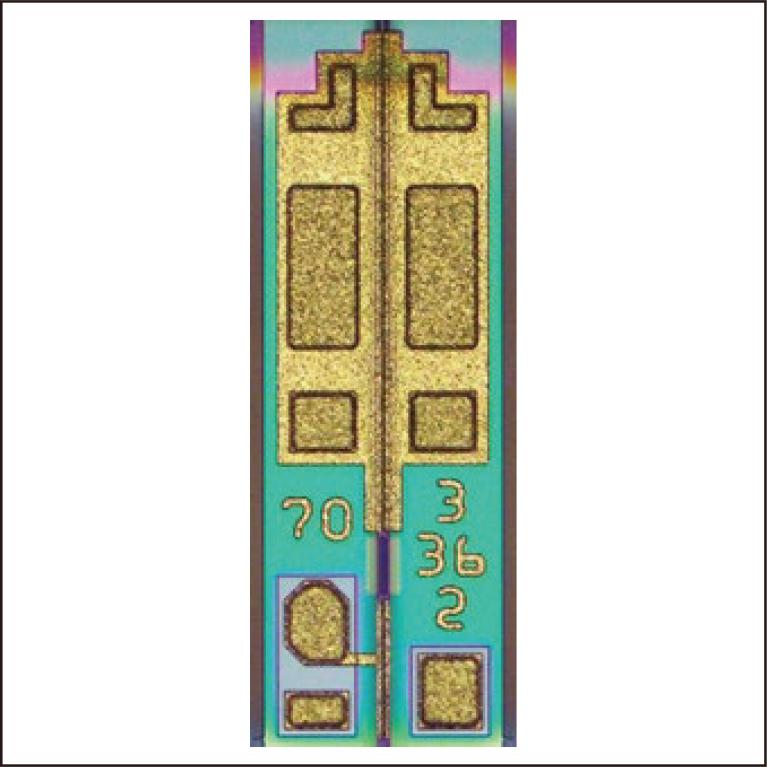
2.8 MB
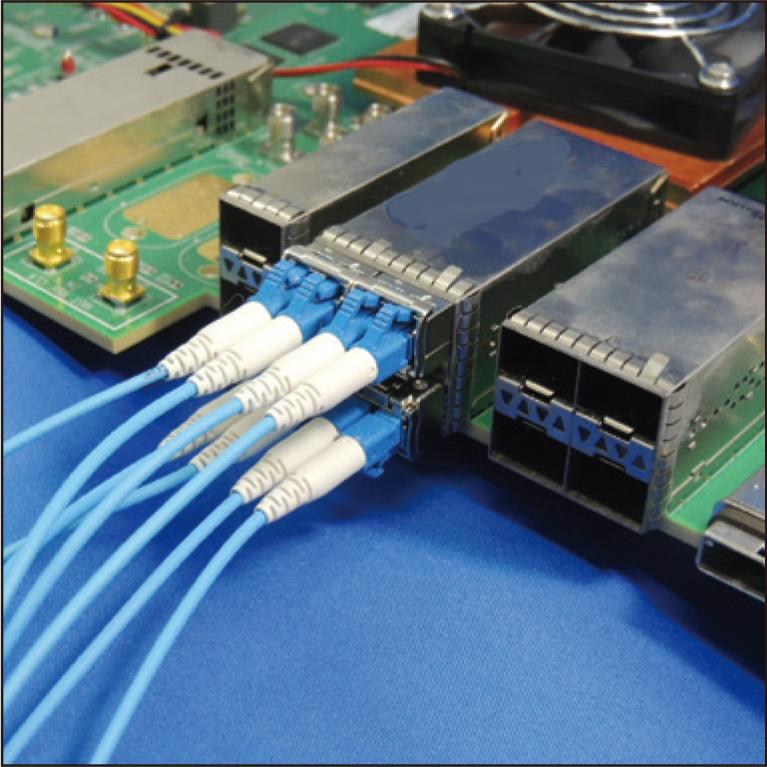
Co-packaged optics (CPO) switches are attracting attention for their ability to reduce power consumption by integrating electrical and optical functions in a single device using silicon photonics (SiPh) technology. By placing the SiPh chip close to the switch ASIC and shortening the electrical interconnection distance, power consumption can be reduced while maintaining the data rate. For optical coupling with a surface coupling type CPO module in the limited space, new optical interconnection components with a low profile, high density, low loss, and high reliability are necessary. For this purpose, we demonstrated a 72-fiber, two-dimensional optical fiber array with a 90-degree bend (2D-FBGE (FlexBeamGuidE)). We developed a stress-free bending technique of polarization-maintaining fiber (PMF). The stress-free bent PMF shows a small radius (R = 2.5 mm), low loss, and high polarization-maintaining characteristics. By combining 90-degree bent optical fibers with a two-dimensional hole array, we have fabricated the 2D-FBGE with a low profile of 5.5 mm, high density of 24 fibers/mm, low insertion loss of less than 0.5 dB, and high polarization-maintaining characteristics of more than 20 dB. Thus, 2D-FBGE offers robust, space-efficient, and scalable fiber coupling applications for surface coupling type CPO modules.
2.8 MB
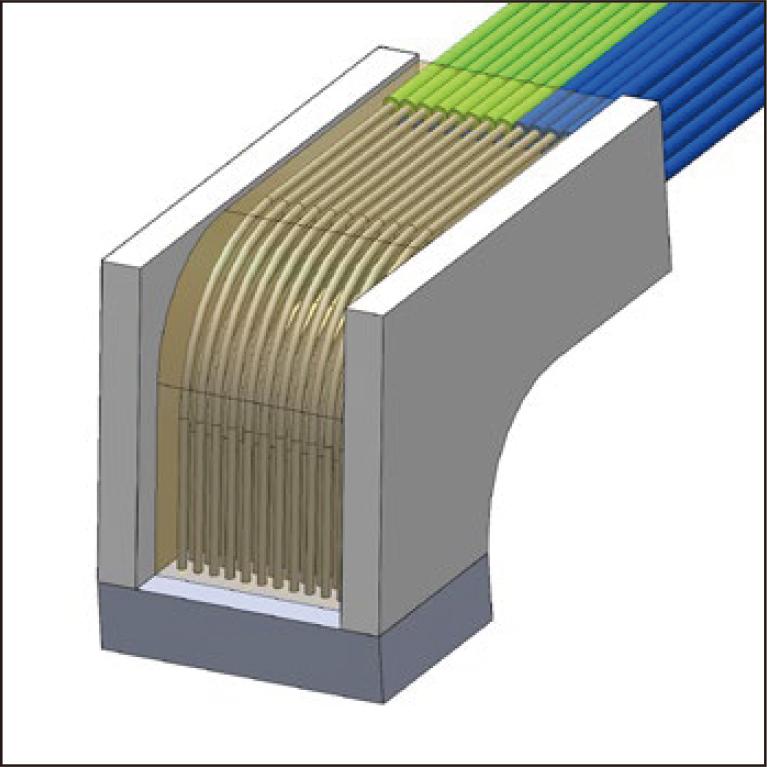
2.8 MB
The transmission capacity of a single submarine cable has been increasing to meet the growing demand for global data traffic, requiring the continuous advancement of optical transmission systems and optical fibers. This paper discusses the submarine fiber that provides the best performance and cost efficiency for the overall system. We found that submarine fibers having a medium core area of 110 to 130 µm2 and attenuation as low as 0.15 dB/km or less are the most preferable for the current several-hundred tera b/s cables based on digital coherent technology. The paper also discusses the prospects for optical fibers with smaller outer diameters and multi-core fibers for the realization of 1 Pb/s and beyond cable by increasing the number of optical fibers installed in the cable.
1.3 MB

1.3 MB
The PureAdvance series includes optical fibers with low attenuation of 0.17 dB/km or less and an enlarged effective core areas of 110 or 125 μm2. These fibers are fully compliant with Recommendation ITU-T G.654.E, and suitable for terrestrial long-haul optical transmission systems. Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. has improved the attenuation of PureAdvance to 0.16 dB/km or lower (typically 0.156 dB/km), and started the commercial supply. With the ultra-low attenuation, transmission performances of terrestrial long-haul optical links can be further improved, enabling high-speed optical transmission at 400 Gb/s and beyond. These fibers will contribute to the realization of high-capacity optical communication in terrestrial long-haul networks.
1.4 MB

1.4 MB
This paper describes newly designed ultra-high-density (UHD) microduct optic cables that are installed into microducts using air-blown technique in order to efficiently build optical transmission capacity in data centers and other facilities. Our microduct cables range from 96-fiber to 864-fiber cables, including 288-fiber cable with flame retardant properties. The UHD microduct cables employ Freeform Ribbon, in which fibers meet and split out repetitively in longitudinal and transverse directions, allowing high fiber density and efficient fusion splicing. In order to enhance the cable-blowing performance, we choose a thin and lightweight cable design with low friction jacket material. These microduct fiber optic cables can be used in various environments, contributing to the efficient and flexible network designs suited to data centers and other customer needs.
2 MB
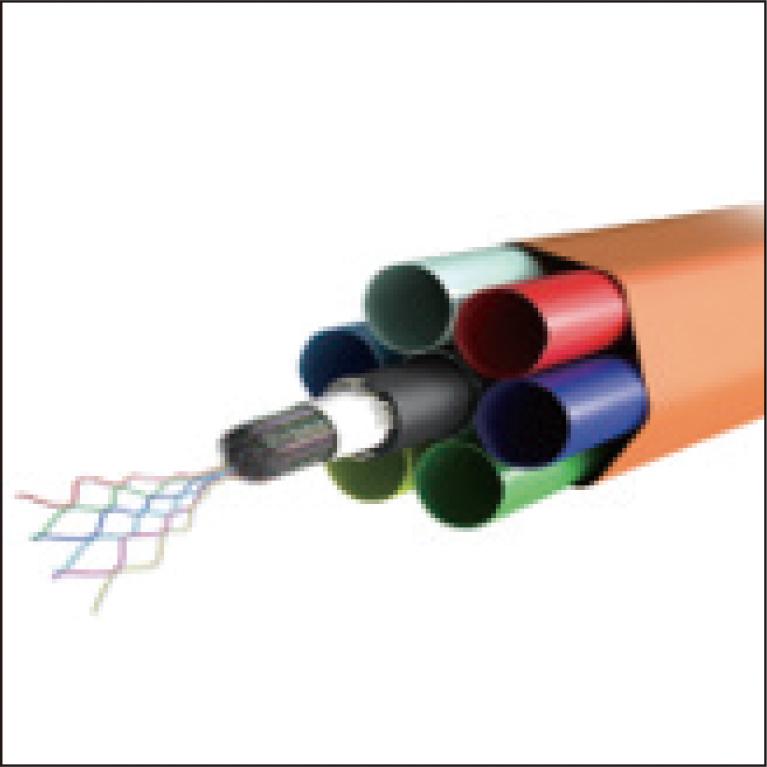
2 MB
This paper describes a new pre-connectorized ultra-high-fiber-count (UHFC) optical fiber cable that has been developed to reduce installation time in data centers. The cable is made of a thin 3456-fiber optical cable consisting of 200 µm Freeform Ribbon fibers and a slotted core. At both ends of the cable, 24-fiber multi-fiber push-on (MPO) connectors are assembled and precisely sealed with a protection sleeve optimally designed for tensile and other mechanical properties. The result of a cable pulling test simulating actual installation was confirmed that the developed cable achieves the same number of optical fibers accommodated in the duct as conventional non-connectorized cables. This cable enables a reduction of connection time by using the MPO connectors instead of mass fusion splicing, and is expected to reduce installation time by about 40% compared to conventional cables.
2.8 MB
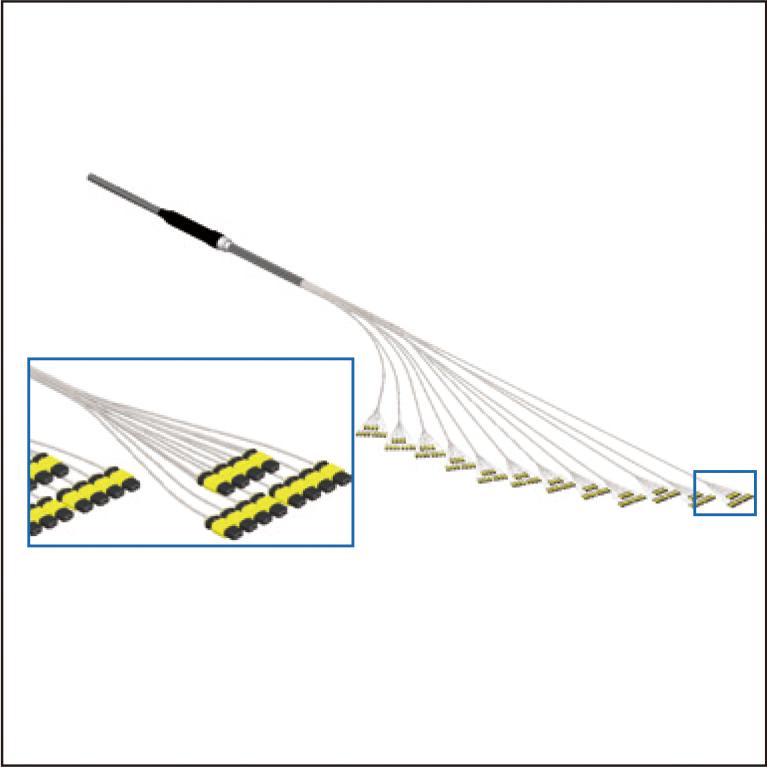
2.8 MB
In multicore fiber (MCF) transmission, low inter-core crosstalk (XT) is crucial to suppress signal quality degradation. This study reveals that the dependence of the XT on fiber bending radius can be evaluated from the longitudinal changes in the bending radius of spooled MCFs with multi-channel OTDR. Using multi-channel OTDR, we also developed a measurement method for backscattered XT, which needs to be considered for bidirectional MCF transmission. With the developed method, we verified the validity of the theoretical prediction of the fiber length dependence of the backscattered XT and clarified the effect of fanout on the bidirectional XT. Our study shows the applicability of multi-channel OTDR for characterizing longitudinal XT change in MCFs and the preferable characteristics of bidirectional transmission in MCF.
2.1 MB
2.1 MB
Next-generation transmission systems using multi-core fiber (MCF) for data center applications require fan-in/fan-out (FIFO) devices with low insertion loss (IL) and high return loss (RL). A fiber bundle FIFO can achieve low IL and high RL by high-precision core eccentricity control of the fiber bundle and physical contact connection between the MCF and the fiber bundle. Although our FIFO is designed to allow only rotational alignment between the MCF and the bundle, the optical characteristics of the fabricated FIFO devices achieved IL of less than 0.3 dB and RL of more than 50 dB.
3 MB
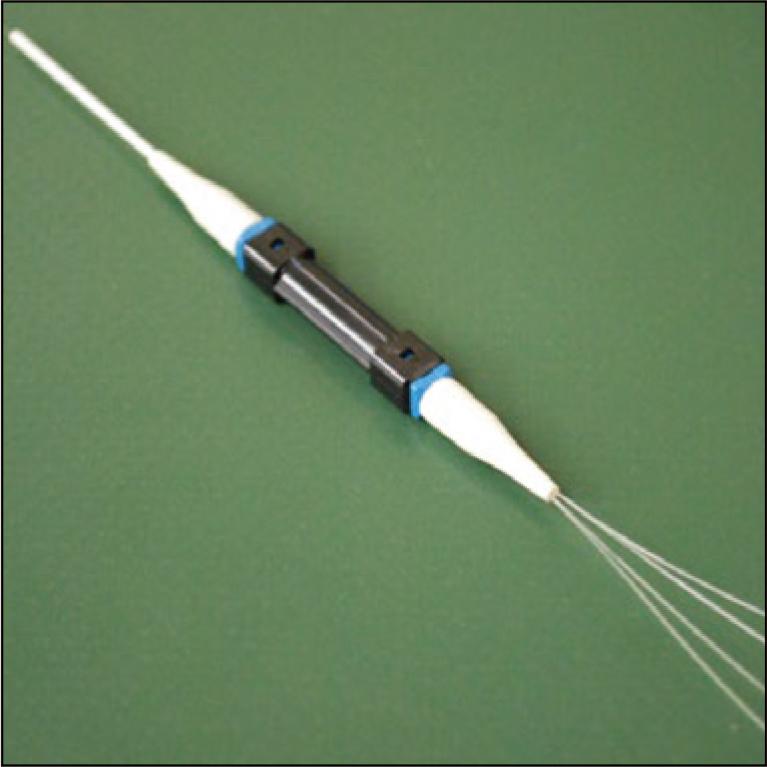
3 MB
The increased transmission loss of optical communication cables in low-temperature environments has been a longstanding issue. However, the mechanism of the loss is still largely unknown. We have developed a technique for evaluating the shape of actual optical cable samples in a low-temperature environment, which was one of the biggest obstacles to elucidating the mechanism. The proprietary technologies include the method to perform low-temperature observation with a simple retrofit mechanism for existing general x-ray computed tomography (XCT) systems and the method for accurately extracting the shape of individual fibers from an indistinct XCT image and quantifying them three-dimensionally. In particular, the latter technology applies not only to optical cables but also to a wide range of cable products, contributing in many ways to the digital transformation promotion of cable product design using big data. This paper introduces an effort to conduct cable evaluation from the viewpoints of both actual measurement and computer-aided engineering, using the shape evaluation of multi-core optical cables in a low-temperature environment as an example.
3.5 MB
3.5 MB
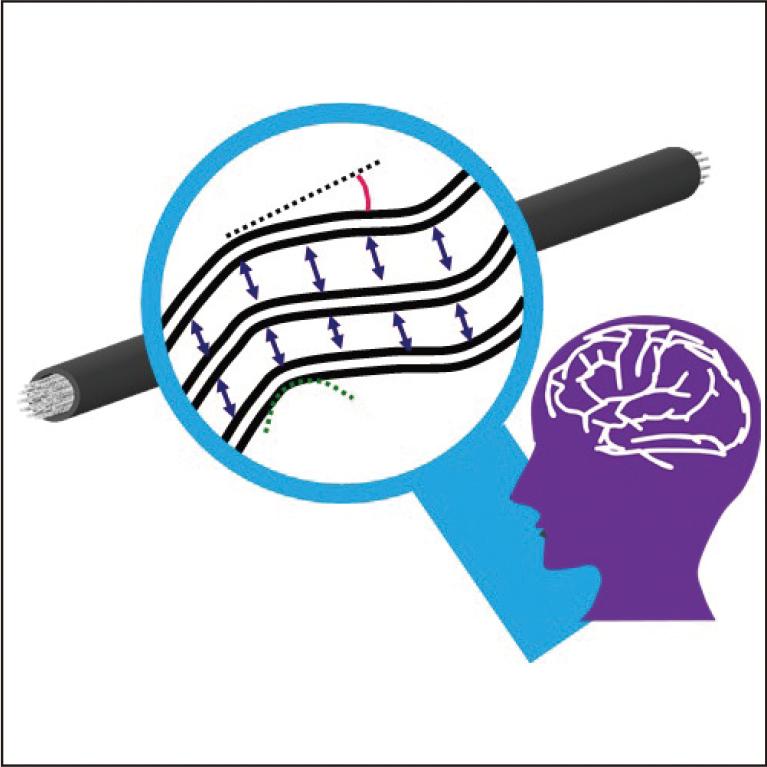
Millimeter-wave GaN HEMTs are expected to be used in higher-capacity wireless communications, but the large nonlinear components such as short-channel effects, have challenges in creating the large-signal models that are essential for amplifier fabrication. In this report, we have developed an innovative model that an artificial neural network (ANN) is applied only to the current source to avoid over-fitting issues. To create this model, pulsed I-Vs/S-parameters measurement data up to 120 GHz were used. The proposed model is the first to demonstrate large-signal power performances at 71 GHz in high accuracy.
1.8 MB
1.8 MB
High-efficiency power amplifiers generate little heat and operate with a small heat dissipation function, making them effective in reducing the size, weight, and cost of communication devices. Since many amplifiers are used in massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO), higher efficiency amplifiers are required, and those based on gallium nitride high electron mobility transistors (GaN HEMTs) are becoming popular particularly for cell phone base station applications. On the other hand, load modulation is attracting attention as an amplifier technology for improving modulation efficiency. Among them, Outphasing amplifiers are known to achieve higher modulation efficiency than conventional Doherty amplifiers. In this study, we conducted a design prototype evaluation of an Outphasing amplifier using our GaN HEMTs. The result confirmed that the higher efficiency of the amplifier reduces power consumption by 1.1 W per amplifier compared to the conventional Doherty amplifier configuration. In a 64 transmitters Massive MIMO base station, a power reduction of 70.4 W is achieved, contributing to the miniaturization of the base station.
1.8 MB
1.8 MB
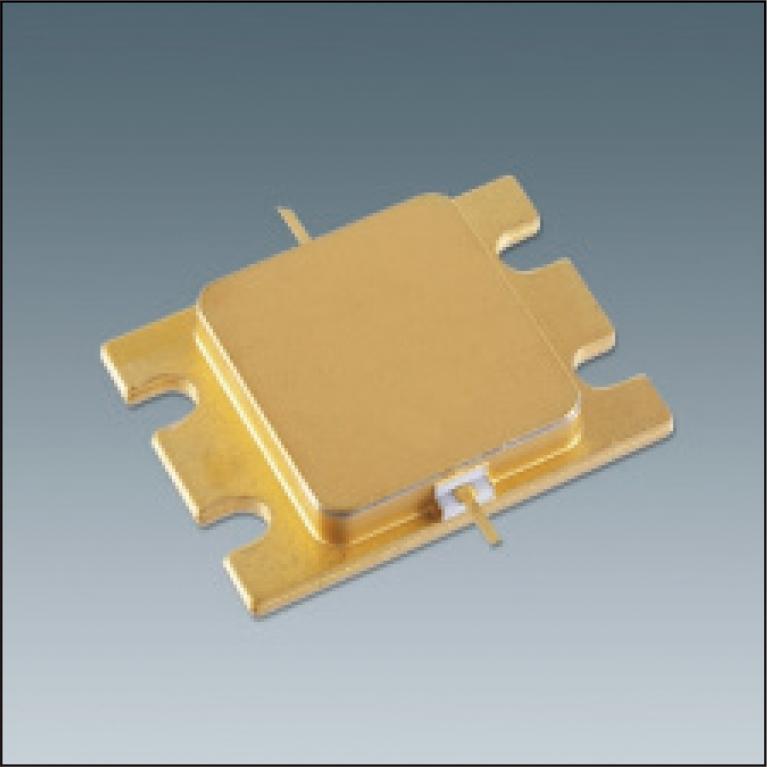
We have developed a high-output, high-efficiency internally matched power amplifier for satellites using gallium nitride high electron mobility transistor (GaN HEMT). Today's wireless communication technology has become indispensable in our lives, not only for Internet and mobile phone communications, but also for electronic payment. Therefore, it has become an indispensable in our lives. Therefore, global information network is growing and the need for satellite communications is increasing as these are less susceptible to natural disasters. The newly developed power amplifier achieves an output power of 100 W and power added efficiency of 60% under CW operation conditions in the C-band (f = 3.7 to 4.2 GHz), the main frequency for satellite communications. The GaN chip used in the development has a confirmed long-term reliability. In terms of both the performance and the reliability, the industry-leading device.
4.1 MB

4.1 MB
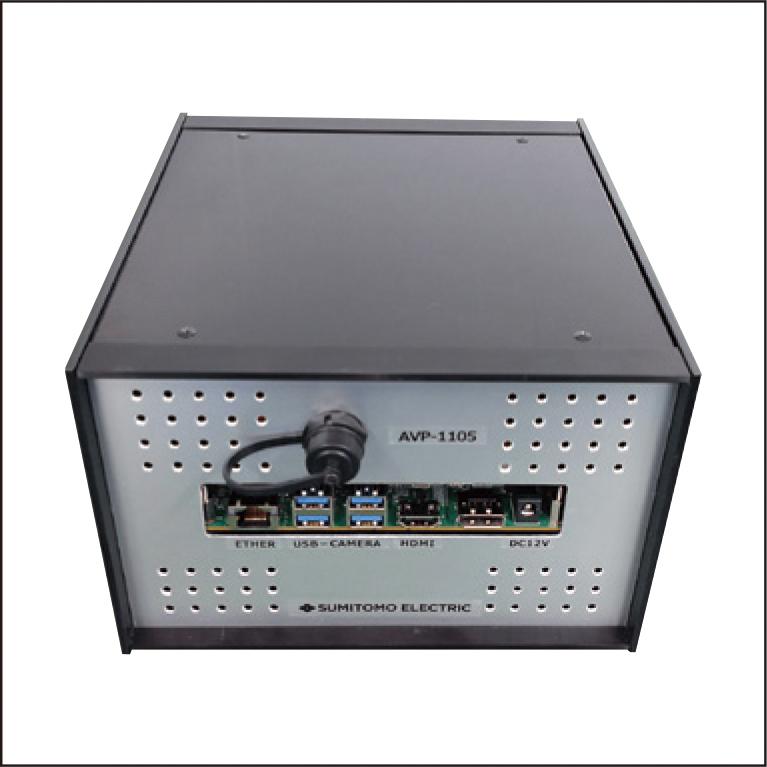
In recent years, AI-based video analysis has been widely used in various fields. Demand for higher definition and wider area viewing has led to the development of cameras with higher resolutions such as 4K and 8K. As a result, the cost of video data transmission, storage, and analysis has increased significantly. In response to this, we have developed a prototype AI-based video processing technology (AVP) that can significantly reduce the amount of video compression data and cloud AI computation cost after transmission. In a field test conducted at a factory, AVP reduced the average bit rate by 92.2% compared to conventional video compression technology, while reducing the AI computation cost on the cloud side, enabling highly accurate analysis of workers' movement flow using high-resolution video.
2.5 MB

2.5 MB
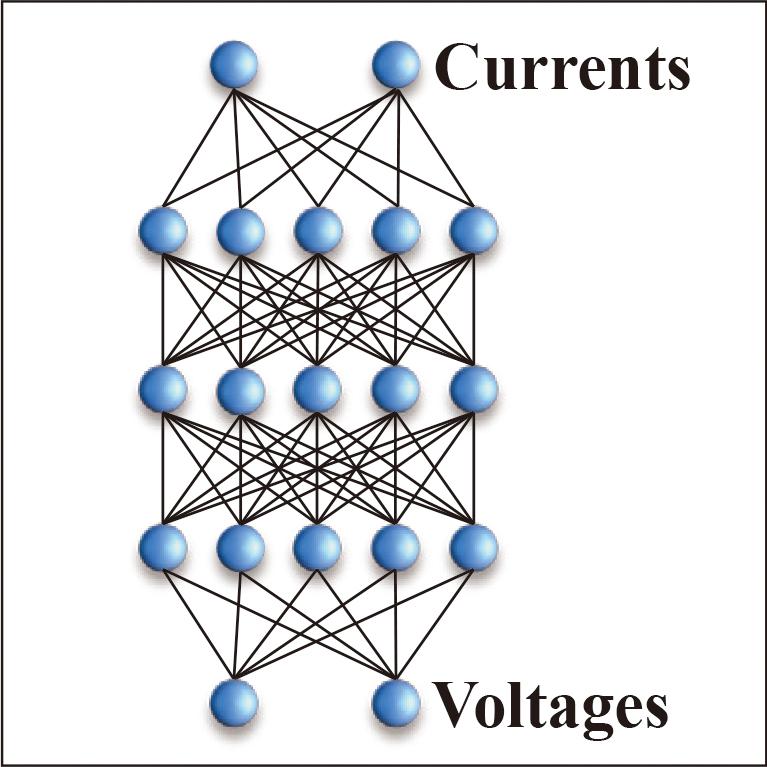
Quantum computing is attracting attention as a technology for solving complex combinatorial optimization problems at high speed. We have been selling delivery planning systems, one of the business support tools for logistics companies, for 20 years and have been conducting research and development of related technologies. The delivery planning systems have a function to calculate efficient delivery routes with low transportation and delivery costs, but it requires complex optimization calculations. With the aim of applying quantum computing to this optimization computation, we are formulating, implementing, and evaluating the performance required for this purpose. In this paper, we report the findings of the validation of the formulation by comparing the results obtained using the Ising machine and conventional computers.
1.6 MB

1.6 MB
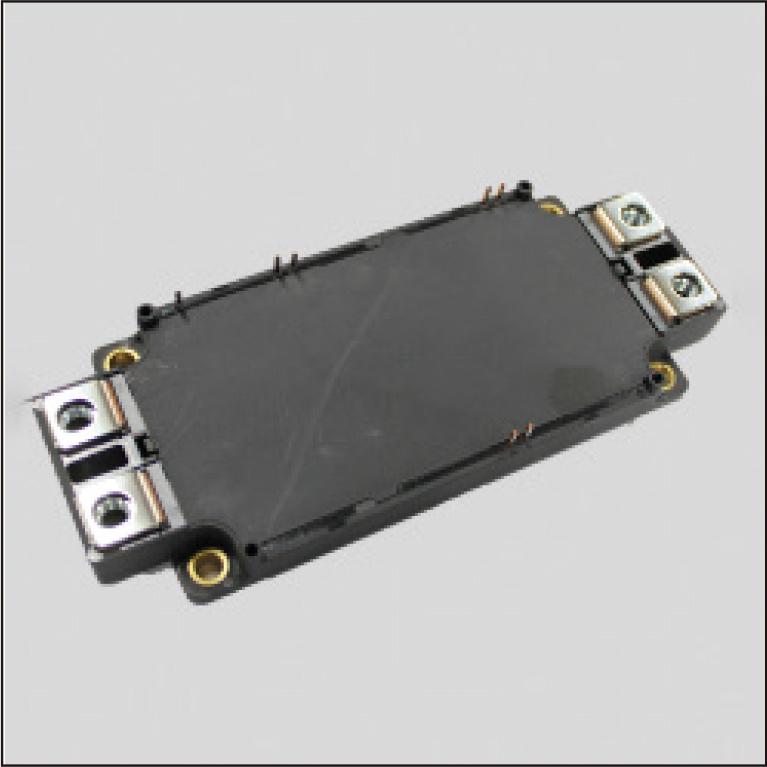
In recent years, the importance of improving the efficiency of power devices used for electric power control has been increasing. Silicon carbide (SiC) is a wide bandgap semiconductor with superior material properties such as high breakdown electric field and high thermal conductivity. Commercialization of SiC MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor) has already begun, and the market size is expected to expand further in the future although Silicon (Si) is mainly used for power devices currently. We have been developing a low on-resistance “V-groove” trench MOSFET (VMOSFET), which uses the patented crystal face as the channel region. In addition to the transistor technology, we have been developing the full SiC modules with the VMOSFET. This report introduces the feature, the electrical characteristics, and the reliability test results of the full SiC power module (1200 V 400 A). The module package has compatibility with Silicon (Si) power module package and is designed for easy replacement for existing users of Si power modules.
1.3 MB

1.3 MB
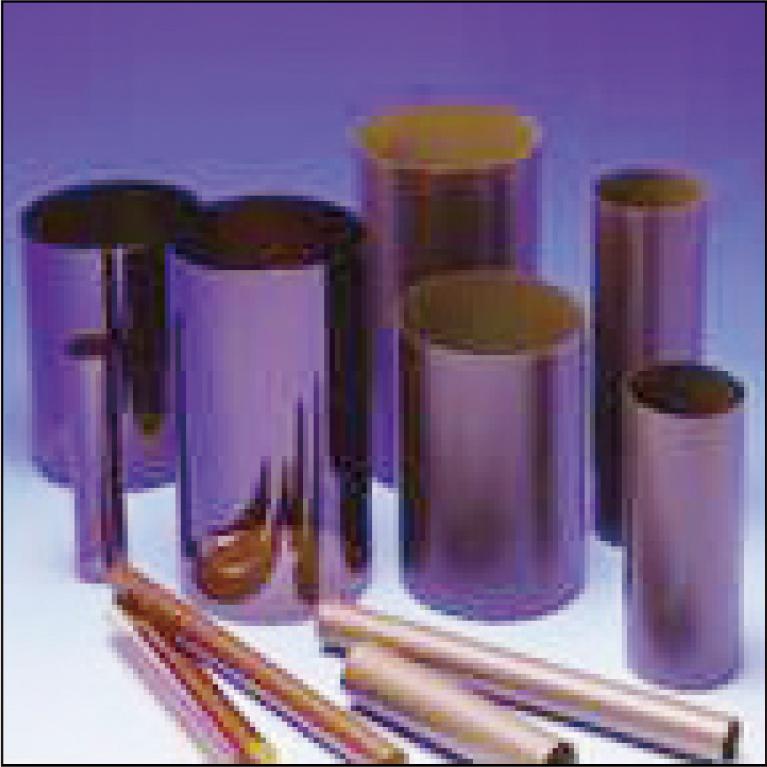
Since 1993, Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. has been manufacturing polyimide fuser rollers, important parts for laser beam printers (LBPs). In recent years, we have developed a high thermo-conductive fuser roller applicable to high-speed printing systems. It uses a composite material that combines carbon nanofiber with high thermal conductivity and tough polyimide resin. Carbon nanofiber is an excellent thermal conductor, but is subject to regulation due to the high risk of residuals when taken into the body. As an alternative to carbon nanofiber, we have developed a new fuser roller using graphite filler, which is also a carbon-based filler.
1.9 MB

1.9 MB
With the recent miniaturization of electronic equipment, there is an increasing demand for high-density wiring in flexible printed circuits (FPC). We have developed a circuit formation technology using a semi-additive process that uses fine-pitch, high-aspect plating. The plating technology has enabled us to establish a manufacturing method for the fine-pitch FPCs that cannot be realized by conventional etching-based circuit formation processes. By applying this technology, mass production of actuator coils for image stabilization of high-performance smartphone cameras has been realized. This paper reports on the circuit formation technology using the semi-additive method and examples of its application to actuator coils, and introduces the latest developments.
1.6 MB
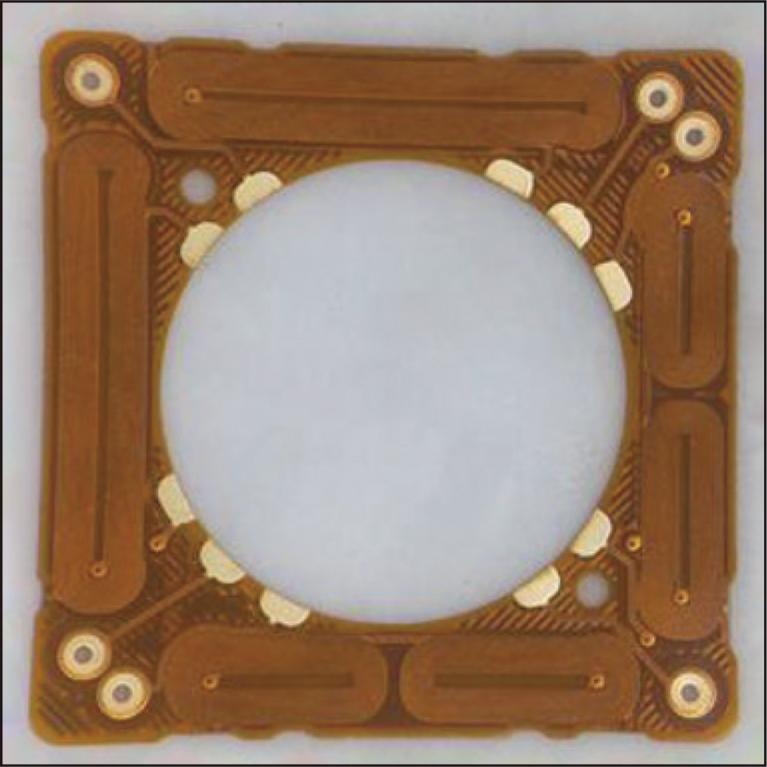

1.6 MB
In order to achieve carbon neutrality, there is a growing trend to use renewable energy as the main power source. However, with an increase in the use of renewable energy, the power system has become congested, making it difficult to connect other new power sources. To solve this problem, Japanese Connect and Manage is being developed to review conventional methods and address power system congestion. Moreover, the dynamic rating is being considered a new operational technology. To realize these concepts, a real-time monitoring system is needed to monitor the conditions of overhead transmission lines and the environment around transmission towers. This system will play an important role as renewable energy will be introduced in large quantities in the future. We have been developing an overhead transmission line monitoring system for the large-scale introduction of renewable energy. This paper introduces the features of our developed system and equipment.
1.5 MB
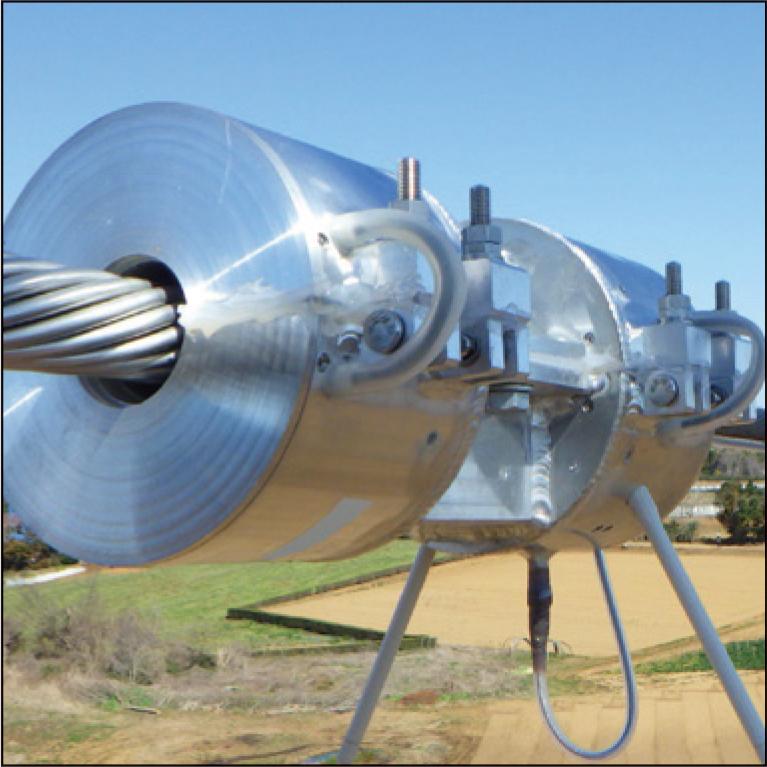

1.5 MB
Sumitomo Electric Toyama Co. Ltd. is aiming to apply Celmet, a porous metal product, as a current collector for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC). NiCo Celmet is particularly suitable for cathode current collectors as it forms conductive oxides in a high-temperature and high-oxidant atmosphere. We reported that fuel cells using the NiCo Celmet exhibit high power density even without gas flow channels in the interconnector because of its high gas diffusivity. In this study, to elucidate the mechanism of high power density, we investigated the influence on DC resistance by applying Celmet as a current collector. We clarified that the contactability between the cell and Celmet is improved by shaping Celmet along the warp of the cell. Moreover, we found that NiCo Celmet can maintain good contactability as its oxidation expansion applies pressure from the inside of the stack.
2.1 MB
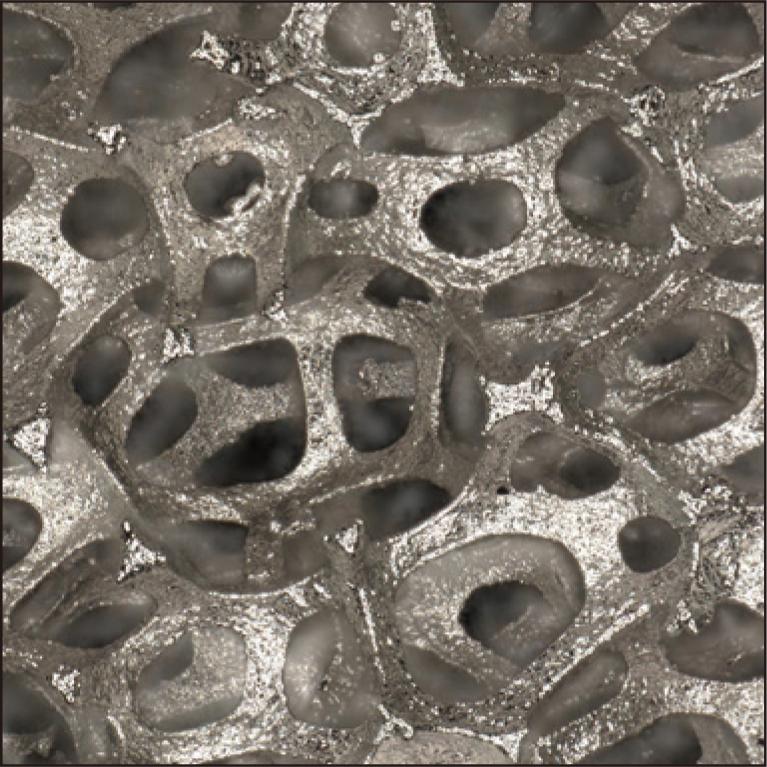

2.1 MB
Due to the increasing demand for carbon neutrality and resource saving, there is a demand for smaller and lighter spring products used in automobile engines, clutches, and other parts. As a result, it is necessary to increase the strength of spring materials. Conventionally, materials have been developed with the policy of increasing fatigue strength equating to increasing hardness. Spring materials, which require the highest fatigue strength among all metal materials, have reached a plateau, and a new approach that considers the environment in which the materials are used is becoming necessary. This paper describes the performance of a newly designed high-strength oil-tempered wire product.
1.8 MB
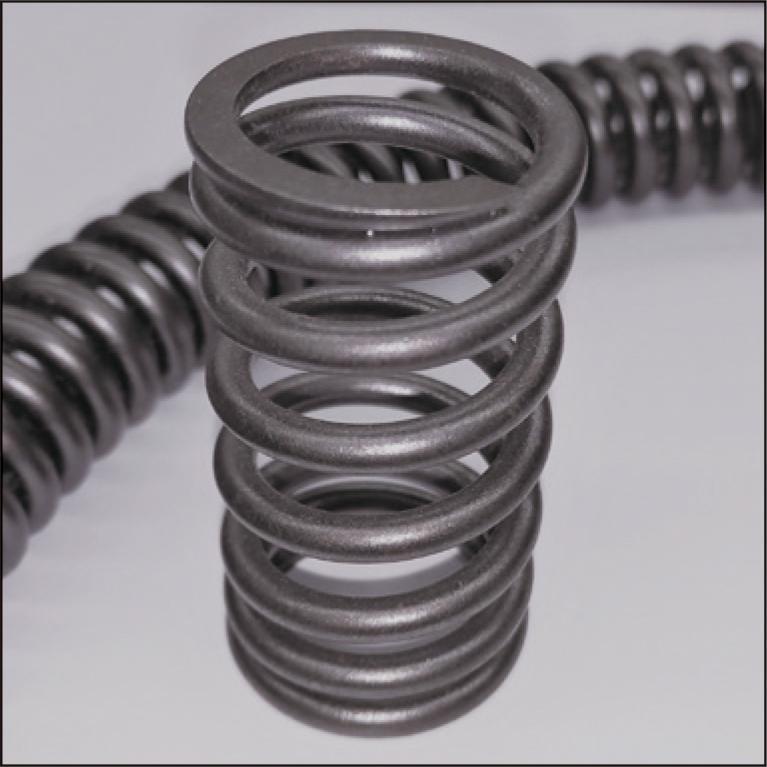

1.8 MB
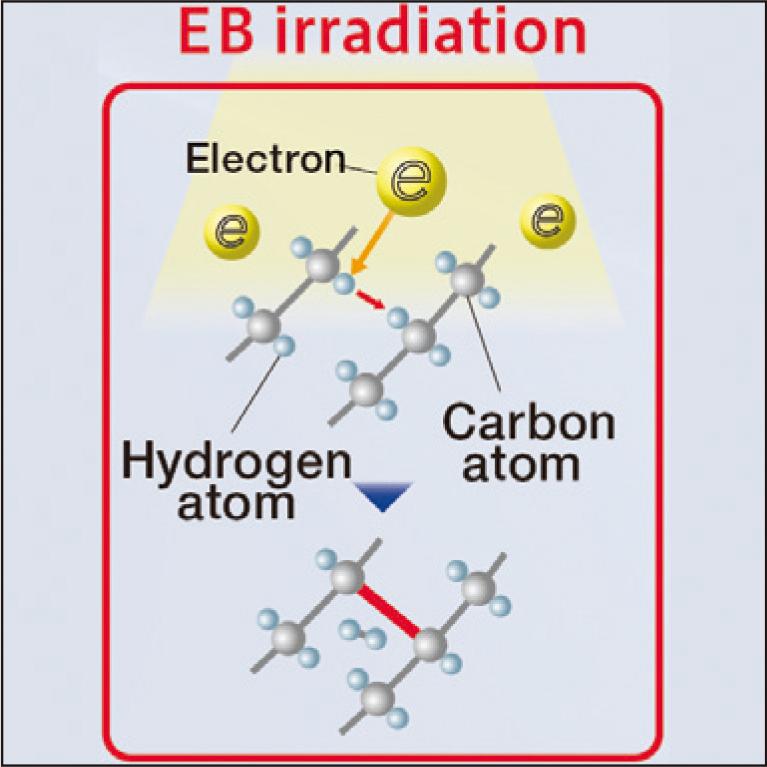
Polyethylene (PE) is one of the polymers widely used in industry. PE is frequently used as a processing material because it is easily cross-linked by electron beam irradiation and its heat resistance is expected to be improved. This paper describes the mechanism of electron beam crosslinking of PE and its effect on PE. The property changes observed in cross-linked PE are also presented.
1 MB
1 MB
Copyright of the paper contained in SUMITOMO ELECTRIC TECHNICAL REVIEW belongs to Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.
The paper is to be used solely for private, reference purpose, and reproduction without the permission of the copyright holder is prohibited.
Meet the Authors of the SUMITOMO ELECTRIC TECHNICAL REVIEW
We at Sumitomo Electric Group are driven to pursue technological innovations to create value for a better world.
Learn more
